Application of phosphate-solubilizing bacteria in soybean cultivation: a mini-review
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14295/bjs.v5i2.843Keywords:
soybean, phosphorus, phosphate-solubilizing bacteria, productivity, soil fertilityAbstract
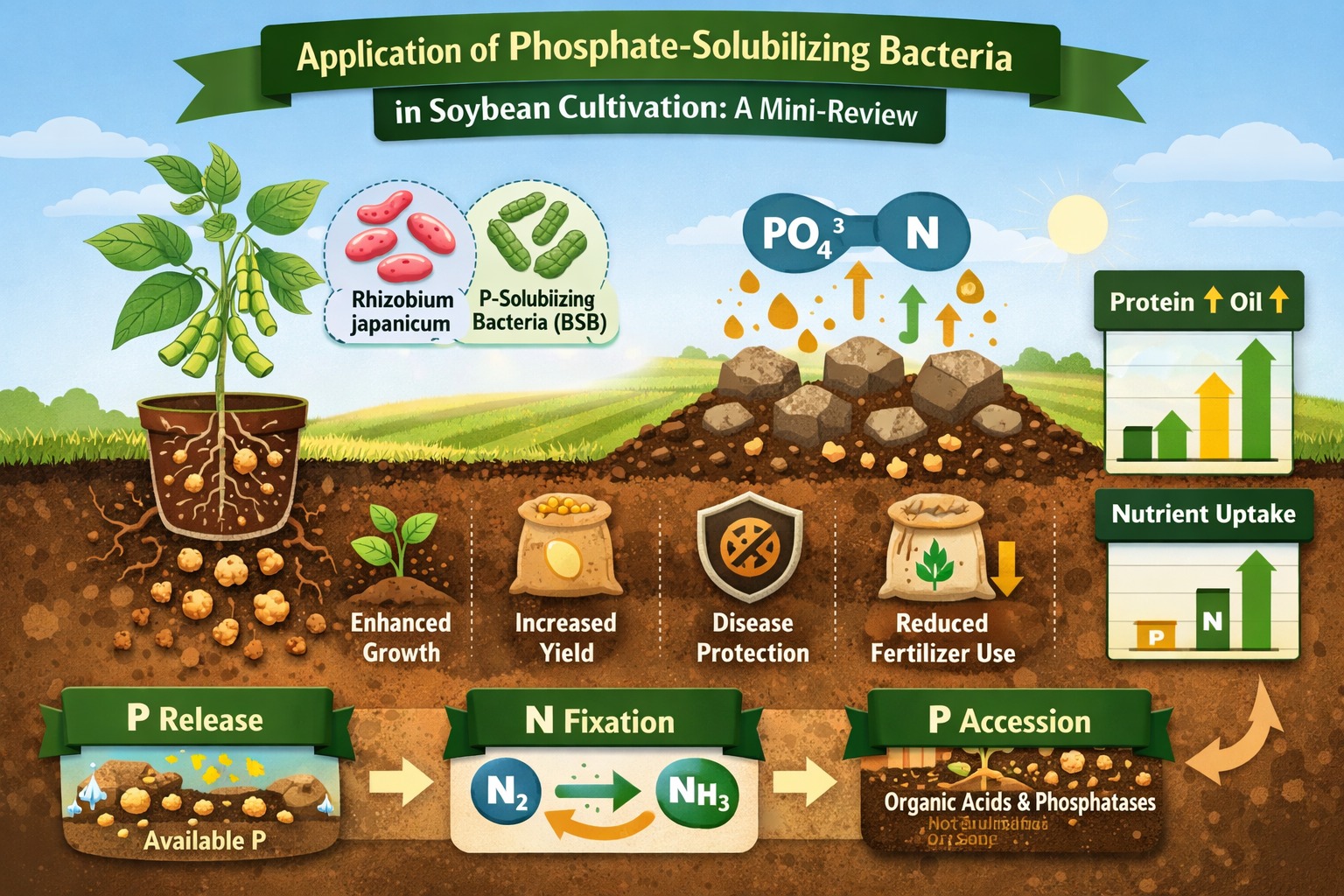
Brazilian agriculture plays a strategic role in the national economy, with Brazil standing out as one of the world’s leading soybean (Glycine max L.) producers. Despite its economic relevance, soybean productivity is constrained by several factors, including high production costs, dependence on non-renewable inputs, adverse climatic conditions, and particularly the low fertility of tropical soils, especially phosphorus (P) deficiency. In this context, the use of phosphate-solubilizing bacteria (PSB) emerges as a sustainable alternative to enhance phosphorus availability and uptake by plants, thereby reducing dependence on chemical phosphate fertilizers. This study aims to review the scientific literature on the application of PSB in soybean cultivation, emphasizing their mechanisms of action, effects on phosphorus uptake, and impacts on plant growth and productivity.
References
Abreu, C. S., Figueiredo, J. E. F., Oliveira, C. A., Santos, V. L., Gomes, E. A., Ribeiro, V. P., Barros, B. A., Lana, U. G. P., & Marriel, I. E. (2017). Maize endophytic bacteria as mineral phosphate solubilizers. Genetics and Molecular Research, 16(1), 1-13. http://dx.doi.org/10.4238/gmr16019294
Ahuja, A., Ghosh, S. B., & D’Souza, S. F. (2007). Isolation of a starch utilizing, phosphate solubilizing fungus on buffered medium and its characterization. Bioresource Technology, 98(17), 3408-3411. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2006.10.041
Akhila, G., Raghuveer, M,M Ranjitha, S., Krishna Chaitanya, A. (2025). Effect of phosphorous levels and PSB strains on growth, yield and nutrient uptake of soybean (Glycine max L.). Plant Archives, 25(2), 2182.
Alves, L., Mendonza, E. A., & Silva Filho, G. N. (2002). Microrganismos solubilizadores de fosfatos e o crescimento de pinus e eucalipto. Revista Brasileira de Ciência do Solo, 36(4), 939-947. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-06832002000400011
Barbosa, V. C. R., & Brisola, M. V. (2024). Além dos campos: as prospecções tecnológicas sustentáveis da EMBRAPA para o agronegócio brasileiro. Revista de Economia e Sociologia Rural, 62(3), e270441. https://doi.org/10.1590/1806-9479.2023.270441pt
Barbosa, M. F., Sales, R. M. M., Galarza, F. A. D., Kruger, C. Q., Fávaro, L. C. L., & Quirino, B. F. (2025). Biological resources driving productivity: bioinputs for sustainable plant agriculture in Brazil. Sustainable Microbiology, 2(3). https://doi.org/10.1093/sumbio/qvaf011
Bevilaqua, G. A. P., Silva Filho, P. M., & Possenti, J. C. (2002). Aplicação foliar de cálcio e boro e componentes de rendimento e qualidade de sementes de soja. Ciência Rural, 32(1), 31-34.
Bittencourt, C. D., Messias, M., Wendland, A., & Brito, E. P. (2024). Phosphate-solubilizing inoculant improves agronomic performance of common bean with reduced phosphate fertilizer dose. Journal of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 24, 5815-5828. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-024-01943-2
Boro, M., Sannyasi, S., Chettri, D., & Verma, A. K. (2022). Microorganisms in biological control strategies to manage microbial plant pathogens a review. Archives of Microbiology, 204. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-022-03279-w
Büll, L. T., Forli, F., Tecchio, M. A., & Corrêa, J. C. (1998). Relação entre fósforo extraído por resina e resposta da cultura do alho vernalizado à adubação fosfatada em cinco solos com e sem adubação orgânica. Revista Brasileira de Ciência do Solo, 22(3), 459-470. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-06831998000300012
Cabrera, E. V. R., Espinosa, Z. Y. D., & Pino, A. F. S. (2024). Use of phosphorus-solubilizing microorganisms as a biotechnological alternative: A review. Microorganisms, 12(8), 1591. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12081591
Charana, B., & Yoon, M-H. (2012). Prospectus of phosphate solubilizing microorganisms and phosphorus availability in agricultural soils: A review. African Journal of Microbiology Research, 6(37), 6600-6605. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJMR12.889
Chen, J., Zhao, G., Wei, Y., Dong, Y., Hou, L., & Jiao, R. (2021). Isolation and screening of multifunctional phosphate solubilizing bacteria and its growth-promoting effect on Chinese fir seedlings. Scientific Reports, 11, 9081. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-88635-4
Chien, S. H., & Menon, R. G. (1995). Factors affecting the agronomic effectiveness of phosphate rock for direct application. Fertilizer Research, 41, 227-234.
Conab. (2025). Companhia Nacional de Abastecimento, safra de grãos 2024/25. Available: https://www.gov.br/conab/pt-br/assuntos/noticias/producao-de-graos-na-safra-2025-26-esta-estimada-em-354-4-milhoes-de-toneladas. Accessed on January 27, 2026.
Copeland, C., Schulze-Lefert, P., & Ma, K-W. (2025). Potential and challenges for application of microbiomes in agriculture. The Plant Cell, 37(8). https://doi.org/10.1093/plcell/koaf185
Coutinho, R. R. (2018). Pochonia chlamydosporia: controle de Meloidogyne javanica em soja, associação com culturas de cobertura e interação com bactérias fixadoras de nitrogênio e com o pH do solo. Tese (Doutorado em Fitopatologia) - Universidade Federal de Viçosa. Viçosa, Brasil, 91 f.
Crespo, Â. L. B. et al. (2024). Assessment of soil persistence and field efficacy of Metarhizium applied for soybean insect pest control. Journal of Fungi, 10(3), 216, 2024. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof10030216.
Dey, G., Banerjee, P., Sharma, R. K., Maity, J. P., Etesami, H., Shaw, A. K., Huang, Y-H., Huang, H-B., & Chen, C-Y. (2021). Management of phosphorus in salinity-stressed agriculture for sustainable crop production by salt-tolerant phosphate-solubilizing bacteria – A review. Agronomy, 11, 1552. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11081552
Duarte, A. L. A. (2019). Virulência de fungos entomopatogênicos contra Helicoverpa armigera em soja. Revista Caatinga, 32(2), 425-434. https://doi.org/10.1590/1983- 21252019v32n215rc
El Batti, M. M., Machado, P. G., Hawkes, A., & Ribeiro, C. O. (2023). Land use polices and their effects on Brazilian farming production. Journal of Nature Conservation, 73, 126373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnc.2023.126373
Feng, Y., He, J., Zhang, H., Jia, X., Hu, Y., Ye, J., Gu, X., Zhang, X., & Chen, H. (2024). Phosphate solubilizing microorganisms also improve plant disease resistance, adaptability, and survival. Frontiers in Microbiology, 14. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2023.1320853
Filho, W. L., Salvia, A. L., Dinis, M. A. P., & Mifsud, M. (2023). The central role of climate action in achieving the United Nations’ sustainable development goals. Scientific Reports, 13, 20582. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-47746-w
Goldberg, S. (2008). Interaction of aluminum and iron oxides and clay minerals and their effect on soil physical properties: A review. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 20(11-12), 1181-1207. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103629009368144
Greschuk, L. T., Demattê, J. A. M., Silvero, N. E. Q., & Rosin, N. A. (2023). Asoil productivity system reveals most Brazilian agricultural lands are below their maximum potential. Scientific Reports, 13, 14103. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-39981-y
Hungria, M., & Nogueira, M. A. (2019). Tecnologias de inoculação da cultura da soja: mitos, verdades e desafios. In: Boletim de Pesquisa 2019/2020, 50-62 p.
Hungria, M., Campo, R. J., & Mendes, I. C. (2007). A importância do processo de fixação biológica do nitrogênio para a cultura da soja: componente essencial para a competitividade do produto brasileiro. Embrapa Soja. Documentos, 283, 80 p.
Hungria, M., Nogueira, M. A., & Araujo, R. S. (2013). Co-inoculation of soybeans and common beans with rhizobia and Azospirilla: strategies to improve sustainability. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 49(7), 791-801. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-012-0771-5
Ibrahim, M., Iqbal, M., Tang, Y-T., Khan, S., Guan, D-X., & Li, G. (2022). Phosphorus mobilization in plant-soil environments and inspired strategies for managing phosphorus: A review. Agronomy, 12(10), 2539. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12102539
Javed, A., Ali, E., Afzal, K. B., Osman, A., & Riaz, S. (2022). Soil fertility: Factors affecting soil fertility, and biodiversity responsible for soil fertility. International Journal of Plant, Animal and Environmental Sciences, 12, 021-033. https://doi.org/10.26502/ijpaes.202129
Khan, F., Siddique, A. B., Shabala, S., Zhou, M., & Zhao, C. (2023). Phosphorus plays key roles in regulating plants’ physiological responses to abiotic stresses. Plants, 12(15), 2861. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12152861
Khan, M. S., Zaidi, A., & Wani, P. A. Role of phosphate-solubilizing microorganisms in sustainable agriculture – A review. Agronomy for Sustainable Development, 27, 29-43. https://doi.org/10.1051/agro:2006011
Kour, D., Kour, H., Khan, S. S., Khan, R. T., Bhardwaj, M., Kailoo, S., Kumari, C., Rasool, S., Yadav, A. N., & Sharma, Y. P. (2023). Biodiversity and functional attributes of rhizospheric microbiomes: Potential tools for sustainable agriculture. Current Microbiology, 80(6), 192. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-023-03300-5
Li, J., Lu, J., Wang, H., Fang, Z., Wang, X., Feng, S., Wang, Z., Yuan, T., Zhang, S., & Ou, S (2021). A comprehensive synthesis unveils the mysteries of phosphate-solubulizing microbes. Biological Reviews, 96(6), 2771-2793. https://doi.org/10.1111/brv.12779
Li, C., Zheng, Z., Zhao, Y., Wang, H., Li, P., Xu, J., Jiao, J., Xu, L., Hu, F., & Li, H. (2024). Phosphate-solubilizing microorganisms stimulate physiological responses of perennial ryegrass to phosphorous deficiency with assistance of straw compost. Agronomy, 14(5), 1008. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14051008
Liu-Xu, L., González-Hernández, A. I., Camañes, G., Vicedo, B., Scalschi, L., & Lorens, E. (2024). Harnessing green helpers: Nitrogen-fixing bacteria and other beneficial microorganisms in plant-microbe interactions for sustainable agriculture. Horticulturae, 10(6), 621. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10060621
Loureiro, E. S., Dias Neto, J. A., Pessoa, L. G. A., Adão, D. V., Dias, P. M., Pereira Filho, A. A., & Mateus, J. A. F. (2020). Manejo de Pratylenchus brachyurus com Trichoderma harzianum e Purpureocillium lilacinum na cultura da soja. Research, Society and Development, 9(7), e124973828. http://dx.doi.org/10.33448/rsd-v9i7.3828
Luo, D., Shi, J., Li, M., Chen, J., Wang, T., Zhang, Q., Yang, L., Zhu, N., & Wang, Y. (2024). Consortium of phosphorus-solubilizing bacteria promotes maize growth and changes the microbial community composition of rhizosphere soil. Agronomy, 14(7), 1535. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14071535
Machado, A. W. (2024). Controle biológico de pragas na soja. Agrolink. Available at: Agrolink – Integrated pest management in soybean. Accessed on: August 30, 2025.
Malavolta, E. (2006). Manual de nutrição de plantas. São Paulo, Ceres. 638 p.
Massucato, L. R., Silva, M. B., Mosela, M., Watanabe, L. S., Afonso, L., Marcos, A. W., Nogueira, A. F., SOUsa, N. V., Fendrich, R. C., & Gonçalves, L. S. A. (2025). Enzymatic activity and organic acid profile of phosphate-solubilizing bacterial inoculants and their agronomic effectiveness in soybean. Microorganisms, 13(9), 2016. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13092016
Medina, G. S. (2022). The economics of agribusiness in developing countries: Areas of opportunities for a new development paradigm in the soybean supply chain in Brazil. Frontiers in Sustainable Food Systems, 6. https://doi.org/10.3389/fsufs.2022.842338
Mendes, I. C., & Reis Júnior, F. B. (2003). Microrganismos e disponibilidade de fósforo (P) nos solos: uma análise crítica. Embrapa, Documentos 85, Planaltina.
Meyer, J. R., & Linderman, R. G. (1986). Response of subterranean clover to dual inoculation with vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and a plant growth-promoting bacterium, Pseudomonas putida. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 18(2), 185-190. https://doi.org/10.1016/0038-0717(86)90025-8
Novais, F. R., & Smyth, T. J. (1999). Fósforo em solo e planta em condições tropicais. Viçosa: UFV, 399 p.
Novais, F. R., Álvarez, V. H., Barros, N.F., Fontes, R. L., Cantarutti, R. B., & Neves, J. C. L. (2007). Fertilidade do solo. Viçosa: SBCS, 1017 p.
Oba, L. X. S., Mattos, L. M., Paiva, G. F., Carrasco, N. F., Santos, E. F., & Mota, L. H. C. (2024). Planting fertilization and Metarhizium anisopliae inoculation in the initial growth of sugarcane. Revista de Agricultura Neotropical, 11(1), e7712. https://doi.org/10.32404/rean.v11i1.7712
Olabi, A. G., Shehata, N., Issa, U. H., Mohamed, O. A., Mahmoud, M., Abdelkareem, M. A., & Abdelzaher, M. A. (2025). The role of green buildings in achieving the sustainable development goals. International Journal of Thermofluids, 25, 101002. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijft.2024.101002
Oliveira Júnior, A., Prochnow, L. I., & Klepker, D. (2011). Soybean yield in response to application of phosphate rock associated triple superphosphate. Scientia Agricola, 68(3), 376-385.
Oliveira, C. A., Alves, V. M. C., Casado, I. E., Gomes, E. A., Scotti, M. R., Carneiro, N. P., Guimarães, C. T., Schaffert, R. E., & Sá, N. M. H. (2009). Phosphate solubilizing microorganisms isolated from rhizosphere of maize cultivated in an oxisol of the Brazilian Cerrado Biome. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 41(9), 1782-1787. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2008.01.012
Pan, L., & Cai, B. (2023). Phosphate-solubilizing bacteria: advances in their physiology, molecular mechanisms and microbial community effects. Microorganisms, 11(12), 2904. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11122904
Pavinato, P. S., & Cipriano, P. E. (2025). Optimizing phosphorus use in tropical soils for sustainable farming. Soil Science Cases. https://doi.org/10.1079/soilsciencecases.2025.0009
Raij, B. V. (2011). Fertilidade do solo e manejo de nutrientes. International Plant Nutrition Institute, Piracicaba, 420 p.
Raij, B. V. (1991). Fertilidade do solo e adubação. São Paulo: Ceres; Piracicaba: Potafos, 181-202 p.
Rao, G. E., Nagarjun, P., Lakshmipathi, R. N., & Seddiqui, M. (2024). Effect of different source of organic phosphorus and PSB on growth and productivity of soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merril. International Journal of Research in Agronomy, 7(12), 526-533. https://doi.org/10.33545/2618060X.2024.v7.i12Sh.2255
Rathinasabapathi, B., Liu, X., Cao, Y., & Ma, L.Q. (2018). Phosphate-solubilizing Pseudomonads for improving crop plant nutrition and agricultural productivity. In: Crop Improvement Through Microbial Biotechnology, 363-372 p. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-444-63987-500018-9
Sarmah, R., Sarma, A. K. (2022). Phosphate solubilizing microorganisms: A review. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103624.2022.2142238
Sohome, S., Barman, A., & Solaiman, Z. M. (2022). Rhizobium and phosphate solubilizing bacteria influence the soil nutrient availability, growth, yield, and quality of soybean. Agriculture, 12(8), 1136. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12081136
Silva, D. S., Arima, E. Y., dos Reis, T. N. P., & Rattis, L. (2023a). Temperature effect on Brazilian soybean yields, and farmers’ responses. International Journal of Agricultural Sustainability, 21(1). https://doi.org/10.1080/14735903.2023.2173370
Silva, L. I., Pereira, M. C., Carvalho, A. M. X., Buttrós, V. H., Pasqual, M., & Dória, J. (2023b). Phosphrous-solubilizing microorhanisms: A key to sustainable agriculture. Agriculture, 13(2), 462. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13020462
Silva, T. P., Pinto, L. A. S. R., Pliveira, C. C. L., Ferreira, R., Trogello, E., & Pereira, M. G. (2025a). Phosphorus fractions in different management systems in the Cerrado Goiano. Ambiente & Água – An Interdisciplinary Journal of Applied Science, 20, e3057. https://doi.org/10.4136/ambi-agua.3057
Silva, J. M., Dalbon, V. A., Alves, A. C., Ataíde, C. B., Santos, T. M. C., Costa, M. E. L., & Montaldo, Y. C. (2025b). Bioinputs in sustainable agriculture: benefits, challenges, and pathways for resilient farming systems. Asian Journal of Research in Crop Science, 10(20, 85-97.
Song, C., Wang, W., Gan, Y., Wang, L., Chang, X., Wang, Y., & Yang, W. (2022). Growth propotion ability of phosphate-solubilizing bacteria from the soybean rhizosphere under maize-soybean. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 102(4), 1430-1442. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.11477
Suman, J., Rakshit, A., Ogireddy, S. D., Singh, S., Gupta, C., & Chandrakala, J. (2022). Microbiome as a key player in sustainable agriculture and human health. Frontiers in Soil Science, 2. https://doi.org/10.3389/fsoil.2022.821589
Tall, S., & Meyling, N. V. (2018). Probiotics for plants? Growth promotion by the entomopathogenic fungus Beauveria bassiana depends on nutrient availability. Microbial Ecology, 76(1), 1002-1008. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-018-1180-6
Timofeeva, A., Galyamova, M., & Sedykh, S. (2022). Prospect of using phosphate-solubilizing microorganisms as natural fertilizers in agriculture. Plants, 11(16), 2119. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11162119
Torres, J. L. R., Costa, D. D. A., Pereira, M. G., Guardieiro, L. V. F., Loss, A., Lourenzi, C. R., Gonzalez, A. P., Carvalho, M., & Vieira, D. M. S. (2023). Phosphorus fractionations and availability in areas under different management systems in the cerrado. Agronomy, 13(4), 966. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13040966
UN. (2024). Sustainable Development, The 17 Goals, United Nations. Available at: https://sdgs.un.org/goals. Accessed in: January 22, 2026.
Viruel, E., Erazzú, L. E., Martinez, L. C., Ferrero, M. A., Lucca, M. E., & Sineriz, F. (2014). Inoculation of maize with phosphate solubilizing bacteria: effect on plant growth and yield. Journal of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 14(4), 819-831. http://dx.doi.org/10.4067/S0718-95162014005000065
Wagemans, J., Holtappels, D., Vainio, E., Rabiey, M., Marzachi, C., Herrero, S., Ravanbakhsh, M., Tebbe, C. C., Ogliastro, M., Ayllón, M. A., & Turina, M. (2022). Going viral: Virus-based biological control agents for plant protection. Annual Review of Phytopathology, 60, 21-42. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-phyto-021621-114208
Wahab, A., Muhammad, M., Munir, A., Abdi, G., Zaman, W., Ayaz, A., Khizar, C., & Reddy, S. P. P. (2023). Role or arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in regulating growth, enhancing productivity, and potentially influencing ecosystems under abiotic and biotic stress. Plants, 12(17), 3102. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12173102
Yi, C., Zhu, J., Chen, L., Huang, X., Wu, R., Zhang, H., Dai, X., & Liang, J. (2023). Speciation of iron and aluminium in relation to phosphorus sorption and supply characteristics of soil aggregates in subtropical forests. Forests, 14(9), 1804. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14091804
Yo, H., Wu, X., Zhang, G., Zhou, F., Harvey, P. R., Wang, L., Fan, S., Xie, X., Li, F., Zhou, H., Zhao, X., & Zhang, X. (2022). Identification of the phosphorus-solubilizing bacteria strain JP233 and its effects on soil phosphorus leaching loss and crop growth. Frontiers in Microbiology, 13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2022.892533
Zhu, Y., Xing, Y., Li, Y., Jia, J., Ying, Y., & Shi, W. (2024). The Role of Phosphate-Solubilizing Microbial Interactions in Phosphorus Activation and Utilization in Plant–Soil Systems: A Review. Plants, 12(19), 2686. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13192686
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2026 Alair Diniz da Costa Filho, Hellen Regina Fernandes Batista Ventura, Edson Luiz Souchie, Matheus Vinicius Abadia Ventura

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
1) Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
2) Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.
3) Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work.


