Influence of CuSO₄ application rates during the vegetative stage on agronomic characteristics of Glycine max (L.) Merrill
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14295/bjs.v4i7.758Keywords:
bioaccumulation, copper sulfate, plant development, toxic effect, oxidative effectAbstract
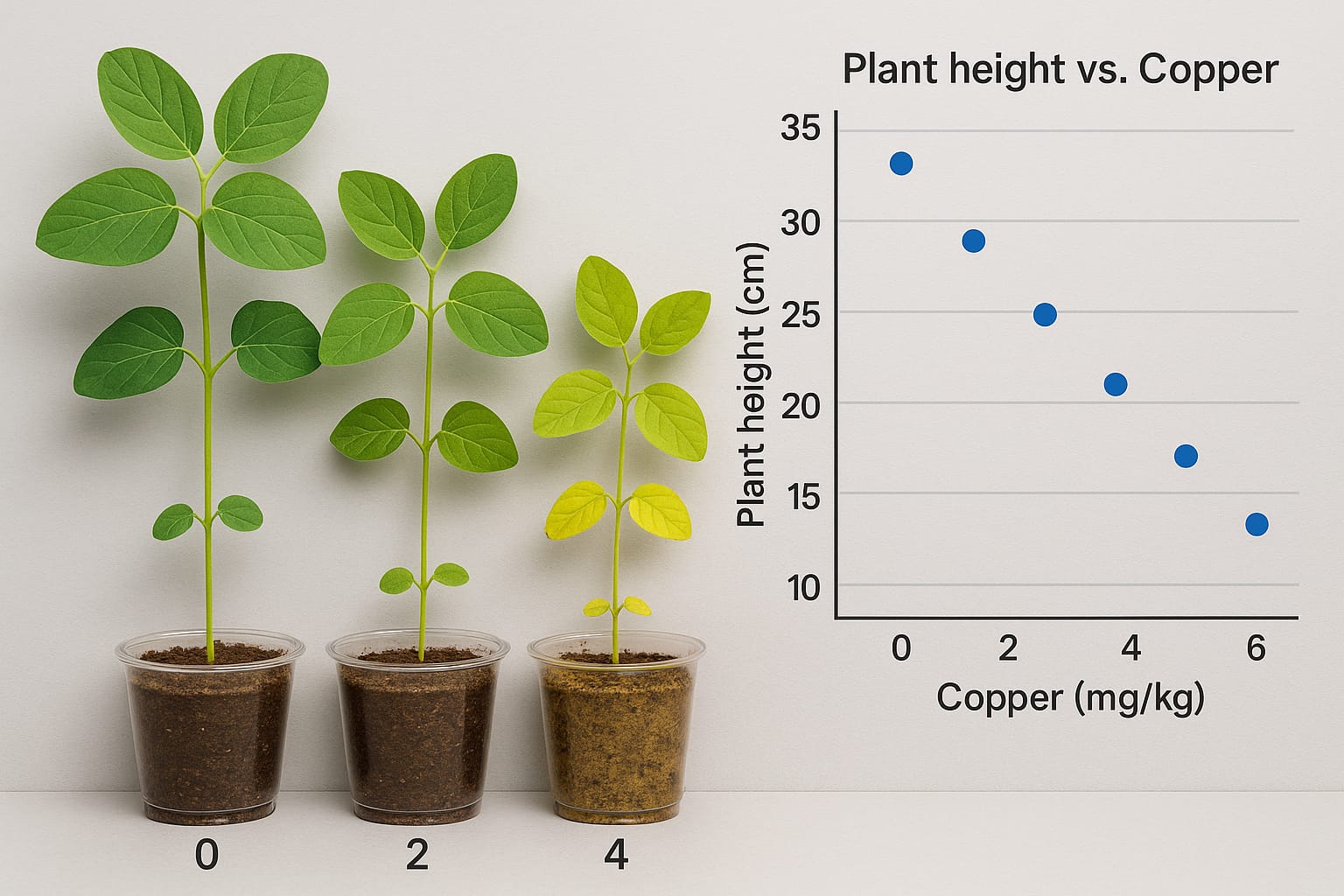
Several micronutrients are essential for the development of agriculturally important crops, including copper (Cu). This study aimed to evaluate the effects of different doses of copper sulfate (CuSO4), expressed as mg L-1 of elemental Cu, on early-maturing soybean during the vegetative phase. Plant parameters such as shoot and root length, fresh and dry biomass of shoots and roots, and Cu bioaccumulation (expressed in mg kg⁻¹) in roots and shoots were assessed. Eight Cu concentrations (0, 5, 15, 35, 85, 100, 125, and 600 mg L-1) were prepared and applied directly into the planting furrow. A precocious soybean cultivar was used. Measurements were taken during the vegetative stage. Significant differences were observed at 100 and 125 mg L-1 doses for root length and root dry mass. The highest Cu bioaccumulation in roots and shoots occurred at 125 mg L-1, while concentrations above this threshold showed toxicity to the early-maturing soybean cultivar. The Cu source applied at varying doses influenced only root development parameters—specifically root length and root dry mass—as well as Cu content accumulated in both roots and shoots during the vegetative growth stage.
References
Amorim, A. V., Lacerda, C. F., Marques, E. C., Ferreira, F. J., Júnior, R. J. C. S., Filho, F. L. A., & Gomes-Filho, E. Micronutrients affecting leaf biochemical responses during pineapple development. Theoretical and Experimental Plant Physiology, 25(1), 70-78. https://www.scielo.br/j/txpp/a/T5bhmtz9czCbgwP8t3B88MF/ DOI: https://doi.org/10.1590/S2197-00252013000100009
Beulter, A. N., & Centurion, J. F. (2004). Compactação do solo no desenvolvimento radicular e na produtividade da soja. Pesquisa Agropecuária Brasileira, 39(6), 581-588. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-204X2004000600010 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-204X2004000600010
Crowe, S. A., Dossing, L. N., Beukes, N. J., Bau, M., Kruger, S. J., Frei, R., & Canfield, D. E. (2013). Atmospheric oxygenation three billion years ago. Nature, 501, 535-538. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12426 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12426
Cruz, F. J. R., Ferreira, R. L. C., Conceição, S. S., Lima, E. U., Neto, C. F. O., Galvaão, J. R., Lopes, S. C., & Viegas, I. J. M. (2022). Copper toxicity in plants: nutritional, physiological, and biochemical aspects. Chapter Plant Response Mechanisms to Abiotic Stresses, 1-13 p.
EMBRAPA – Empresa brasileira de Pesquisa Agropecuária. (2011). Manual de métodos de análise de solo. 2ª Ed., Rio de Janeiro: EMBRAPA Solos, 230 p.
Fageria, N. K. (2001). Adequate and toxic levels of copper and manganese in upland rice, common bean, corn, soybean, and wheat grown on an Oxisol. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 32(9-10), 1659-1676. https://doi.org/10.1081/CSS-100104220 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1081/CSS-100104220
Fageria, N. K. (2007). Micronutrients’ influence on root growth of upland rice, common bean, corn, wheat, and soybean. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 25(3), 613-622. https://doi.org/10.1081/PLN-120003385 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1081/PLN-120003385
Ferreira, D. F. (2019). Sisvar: A computer analysis system to fixed effects split plot type designs. Brazilian Journal of Biometrics, 37(4), 529-535. https://doi.org/10.28951/rbb.v37i4.450 DOI: https://doi.org/10.28951/rbb.v37i4.450
Gomes, D. G., Lopes-Oliveira, P. J., Debiasi, T. V., Cunha, L. S., & Oliveira, H. C. (2021). Regression models to stratify the copper toxicity responses and tolerance mechanisms of Glycine max (L.) Merr. plants. Planta, 253. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-021-03573-9 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-021-03573-9
Gonçalves, F. A. R., Xavier, F. O., Oliveira, T. F., Júnior, J. D. G., & Aquino, L. A. (2017). Aplicação foliar de doses e fontes de cobre e manganês nos teores foliares destes micronutrientes e na produtividade da soja. Cultura Agronômica, 26(3), 384-392. https://doi.org/10.32929/2446-8355.2017v26n3p384-392 DOI: https://doi.org/10.32929/2446-8355.2017v26n3p384-392
Kulikova, A. L., Kuznetsova, N. A., & Kholodova, V. (2011). Effect of copper excess in environment on soybean root viability and morphology. Russian Journal of Plant Physiology, 58(5), 836-843. http://dx.doi.org/10.1134/S102144371105013X DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S102144371105013X
Lequeux, H., Hermans, C., Lutts, S., & Verbruggen, N. (2010). Response to copper excess in Arabidopsis thaliana: Impact on the root system architecture, hormone distribution, lignin accumulation and mineral profile. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 48, 673-682. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2010.05.005 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2010.05.005
Lin, F., Chhapekar, S. S., Vieira, C. C., Silva, M. P., Rojas, A., Lee, D., Liu, N., Pardo, E. M., Lee, Y-C., Pinehiro, J. B., Ploper, L. D., Rupe, J., Chen, P., Wang, D., & Nguyen, H. T. (2022). Breeding for disease resistance in soybean: a global perspective. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 135, 3773-3872. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-022-04101-3 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-022-04101-3
Mataveli, L. R. V., Pohl, P., Mounicou, S., Arruda, M. A. Z., & Szpunar, J. (2010). A comparative study of element concentrations and binding in transgenic and non-transgenic soybean seeds. Metallomics, 2(12), 800-805. https://doi.org/10.1039/c0mt00040j DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/c0mt00040j
Puig, S., Andrés-Colás, N., García-Molina, A., & Peñarrubia, L. (2007). Copper and iron homeostasis in Arabidopsis: Responses to metal deficiencies, interactions and biotechnological applications. Plant Cell Environmental, 30, 271-290. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3040.2007.01642.x DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3040.2007.01642.x
Rai, M., Lngle, A. P., Pandit, R., Paralikar, P., Shende, S., Gupta, I., Biswas, J. K., & Silva, S. S. (2018). Copper and copper nanoparticles: Role in management of insect-pests and pathogenic microbes. Nanotechnology Reviews, 7(4), 303-315. http://dx.doi.org/10.1515/ntrev-2018-0031 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1515/ntrev-2018-0031
Sakai, T., & Kogiso, M. (2008). Soy isoflavones and immunity. Journal of Medical Investigation, 55(3-4), 167-173. https://doi.org/10.2152/jmi.55.167 DOI: https://doi.org/10.2152/jmi.55.167
Shaw, A. K., & Hossain, Z. (2013). Impact of nano-CuO stress on rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings. Chemosphere, 93(6), 906-915. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.05.044 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.05.044
Yuan, M., Wang, S., Chu, Z., Li, X., & Xu, C. (2010). The bacterial pathogen Xanthomonas oryzae overcomes rice defenses by regulating host copper redistribution. The Plant Cell, 22(9), 3164-3176. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.110.078022 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.110.078022
Yusefi-Tanha, E., Fallah, S., Pokhrel, L. R., & Rostamnejadi, A. (2024). Role of particle size-dependent copper bioaccumulation-mediated oxidative stress on Glycine max (L.) yield parameters with soil-applied copper oxide nanoparticles. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 31(20), 28905-28921. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-33070-x DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-33070-x
Yusefi-Tanha, E., Fallah, S., Rostamnejadi, A., & Pokhrel, L. R. (2020). Root system architecture, copper uptake and tissue distribution in soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merr.) grown in copper oxide nanoparticle (CuONP)-amended soil and implications for human nutrition. Plants, 9(10), 1326. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9101326 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9101326
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Richard Breno Sousa Castro, Matheus Vinícius Abadia Ventura, Elizabete Nunes da Rocha, Carlos Frederico de Souza Castro, Antonio Carlos Pereira de Menezes Filho

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
1) Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
2) Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.
3) Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work.


