Comparative analysis of the antibacterial activity of Silver nanoparticles synthesized from leaf extracts of Ocimum sanctum, Coriandrum sativum, Hemidesmus indicus, and Tinospora cordifolia
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14295/bjs.v4i1.686Keywords:
silver nanoparticles, Ocimum sanctum, Coriandrum sativum, Hemidesmus indicus, Tinospora cordifolia, antibacterial activityAbstract
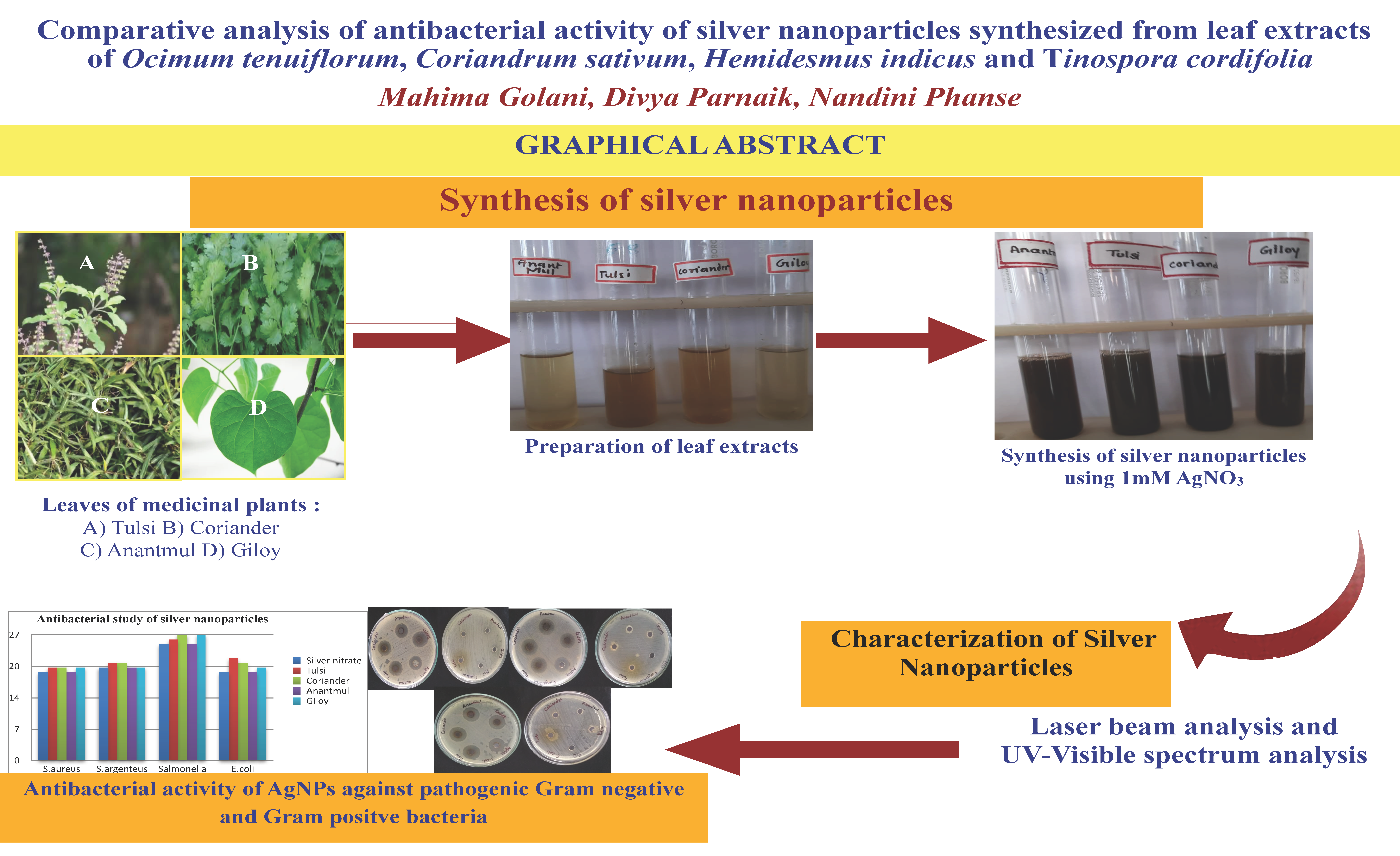
The synthesis of metal nanoparticles using biological resources, such as plant leaves, offers a green, cost-effective, and eco-friendly approach. In this study, 1 mM Silver nitrate solution was mixed with freshly prepared aqueous leaf extracts of each medicinal plant like, “Tulsi (Ocimum sanctum), Coriander (Coriandrum sativum), Anantmul (Hemidesmus indicus) and Giloy (Tinospora cordifolia)” in 1:4 ratios. The mixtures were then incubated at 75 °C for 25 min, forming Silver nanoparticles giving a deep brown color to the solution with Silver in a reduced colloidal form. Laser diffraction and UV-Vis spectroscopy further confirmed the synthesis, with the absorption peak for the nanoparticles observed between 419-438 nm. The antibacterial activity of the synthesized nanoparticles was tested against Gram-positive pathogens, including Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus argenteus, as well as Gram-negative bacteria like Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhi. Comparative analysis showed that nanoparticles synthesized from Tulsi, Coriander, and Giloy extracts demonstrated superior antibacterial efficacy, highlighting their potential for use in biomedical and industrial applications such as wound healing, medical devices, and water purification.
References
Agarwal, S., Ramamurthy, P. H., Fernandes, B., Rath, A., & Sidhu, P. (2019). Assessment of antimicrobial activity of different concentrations of Tinospora cordifolia against Streptococcus mutans: An: in vitro: study. Dental Research Journal, 16(1), 24-28. DOI: https://doi.org/10.4103/1735-3327.249556
Ashraf, A., Zafar, S., Zahid, K., Shah, M. S., Al-Ghanim, K. A., Al-Misned, F., & Mahboob, S. (2019). Synthesis, characterization, and antibacterial potential of silver nanoparticles synthesized from Coriandrum sativum L, Journal of Infection and Public Health, 12(2), 275-281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiph.2018.11.002 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiph.2018.11.002
Begum, H. J., Ramamurthy, V., & Senthil Kumar, S. (2019). Study of synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles from Tinospora cordifolia. The Pharma Innovation Journal, 8(1), 612-615. https://www.thepharmajournal.com/archives/2019/vol8issue1/PartK/8-1-98-800.pdf
Daisy, P., & Saipriya, K. (2012). Biochemical analysis of Cassia fistula aqueous extract and phyto-chemically synthesized gold nanoparticles as hypoglycemic treatment for diabetes mellitus. International Journal of Nanomedicine, 7, 1189-1202. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S26650 DOI: https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S26650
Debnath, M., Khandelwal, M., Lal, P., & Jain, R. (2014). Evaluation of heavy metal distribution and antibacterial activities of medicinal plants Tinospora cordifolia, Ocimum sanctum and Piper nigrum. International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Drug Research, 6(3), 229-234.
https://ijpsdronline.com/index.php/journal/article/view/347
Dey, A., Nandy, S., Mukherjee, A., & Modak, B. K. (2021). Sustainable utilization of medicinal plants and conservation strategies practiced by the aboriginals of Purulia district, India: a case study on therapeutics used against some tropical otorhinolaryngologic and ophthalmic disorders. Environment, Development and Sustainability, 23, 5576-5613. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-020-00833-8
Dhama, K., Tiwari, R., Chakraborty, S., Saminathan, M., Kumar, A., Karthik, K., Wani, M. Y., Amarpal, S. S., & Rahal, A. (2014). Evidence based antibacterial potentials of medicinal plants and herbs countering bacterial pathogens especially in the era of emerging drug resistance: an integrated update. International Journal of Pharmacology, 10(1), 1-43. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3923/ijp.2014.1.43
Jaggi, R. K., Madaan, R., & Singh, B. (2003). Anticonvulsant potential of holy basil, Ocimum sanctum Linn., and its cultures. Indian Journal of Experimental Biology, 41(11), 1329-1333.
Jain, S., & Mehata, M. S. (2017). Medicinal plant leaf extract and pure flavonoid mediated green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their enhanced antibacterial property. Scientific Reports, 7(1), 1-13. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-15724-8
Okafor, F., Janen, A., Kukhtareva, T., Edwards, V., & Curley, M. (2013). Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles, their characterization, application and antibacterial activity. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 10(10), 5221-5238. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph10105221 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph10105221
Pattanayak, P., Behera, P., Das, D., & Panda, S. K. (2010). Ocimum sanctum Linn. A reservoir plant for therapeutic applications: An overview. Pharmacognosy Reviews, 4(7), 95. DOI:10.4103/0973-7847.65323. DOI: https://doi.org/10.4103/0973-7847.65323
Phanjom, P., Sultana, A., Sarma, H., Ramchiary, J., Goswami, K., & Baishya, P. (2012). Plant-mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Elaeagnus latifolia leaf extract. Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructure, 7(3), 1117-1123. https://chalcogen.ro/1117_Phanjom.pdf
Phanse, N. V., Venkataraman, K., Kekre, P. A., Shah, S., & Parikh, S. (2024). Phyto-assisted synthesis of Silver nanoparticles using Tinospora cordifolia leaf extract and their antibacterial activity: An ecofriendly approach. Brazilian Journal of Science, 3(2), 57-65. https://doi.org/10.14295/bjs.v3i2.501 DOI: https://doi.org/10.14295/bjs.v3i2.501
Phanse, N., Venkataraman, K., Mishra, V., Shah, S., & Parikh, S. (2022). Biomediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles from Coriandrum sativum leaf extract: A green approach. International Journal for Modern Trends in Science and Technology, 8(05), 477-480. https://doi.org/10.46501/IJMTST0805072
Pradhan, S. (2013). Comparative analysis of silver nanoparticles prepared from different plant extracts (Hibiscus rosa sinensis, Moringa oleifera, Acorus calamus, Cucurbita maxima, Azadirachta indica) through green synthesis method, Ph.D. Thesis. National Institute of Technology, Rourkela.
Praiwala, B., Priyanka, S., Raghu, N., Gopenath, N., Gnanasekaran, A., Karthikeyan, M., & Basalingappa, K. M. (2018). In vitro anti-bacterial activity of Tinospora cordifolia leaf extract and its phytochemical screening. Journal of Biomedical Sciences, 5(2), 10-17.https://doi.org/10.3126/jbs.v5i2.23633 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3126/jbs.v5i2.23633
Prajwala, B., Gopenath, T. S., Prasad, N., Raviraja, S., & Basalingappa, K. M. (2021). Green synthesis of silver nanoparticle by using Tinospora cordifolia leaf extract and its antimicrobial property. International Journal of Pharmaceutical Science & Research, 12(3), 1881-1886. https://doi.org/10.13040/IJPSR.0975-8232.12(3).1881-86 DOI: https://doi.org/10.13040/IJPSR.0975-8232.12(3).1881-86
Prajwala, B., Raghu, N., Gopenath, T. S., & Basalingappa, K. M. (2019). Guduchi: its medicinal properties. Journal of Plant Physiology & Pathology, 3(2), 1-6.
Sandhu, A., Bhardwaj, N., Gupta, R., & Menon, V. (2013). Antimicrobial activity and photochemical screening of Tinospora cordifolia and Euphorbia hirta. International Journal of Applied Biology and Pharmaceutical Technology, 3(4), 310-16. https://imsear.searo.who.int/handle/123456789/164433
Sathyavati, R., Krishna, M., Rao, S., Sarita, R. & Rao, D. (2010). Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Coriandrum sativum leaf extract and their application in nonlinear optics, Journal of Advanced Science Letter, 3(2), 138-143. https://doi.org/10.1166/asl.2010.1099 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1166/asl.2010.1099
Senthilkumar, N., Aravindhan, V., Ruckmani, K., & Potheher, I. V. (2018). Coriandrum sativum mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles and evaluation of their biological characteristics. Materials Research Express, 5(5), 055032. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/aac312 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/aac312
Singh, K., & Panghal, M. (2014). Antibacterial activity of synthesized silver nanoparticles from Tinospora cordifolia against multi drug resistant strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from burn patients. Journal of J Nanomedicine & Nanotechnology, 5(2), 1-6.
Singh, K., Panghal, M., Kadyan, S., Chaudhary, U., & Yadav, J. P. (2014). Antibacterial activity of synthesized silver nanoparticles from Tinospora cordifolia against multi drug resistant strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from burn patients. Journal of Nanomedicine and Nanotechnology, 5(2), 1-6. https://doi.org/10.4172/2157-7439.1000192 DOI: https://doi.org/10.4172/2157-7439.1000192
Song, J. Y., Jang, H. K., & Kim, B. S. (2009). Biological synthesis of gold nanoparticles using Magnolia kobus and Diopyros kaki leaf extracts. Process Biochemistry, 44(10), 1133-1138. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2009.06.005
Tailor, G., Yadav, B. L., Chaudhary, J., Joshi, M., & Suvalka, C. (2020). Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Ocimum canum and their anti-bacterial activity. Biochemistry and Biophysics Reports, 24, 100848. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrep.2020.100848 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrep.2020.100848
Thakur, S., Kaurav, H., & Chaudhary, G. (2021). Hemidesmus indicus (Anantmool): A potential traditional plant with antivenom activity. International Journal of Research of Ayurveda Pharmacy, 12(3), 106-112. http://dx.doi.org/10.7897/2277-4343.120384 DOI: https://doi.org/10.7897/2277-4343.120384
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Mahima Golani, Divya Parnaik, Nandini Phanse

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
1) Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
2) Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.
3) Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work.


