Molecular docking, dynamics, and drug-likeness studies of alprazolam derivatives as a potent anxiolytic drug against GABAA receptors
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14295/bjs.v4i1.681Keywords:
GABAA antagonist, alprazolam, molecular docking, drug-likenessAbstract
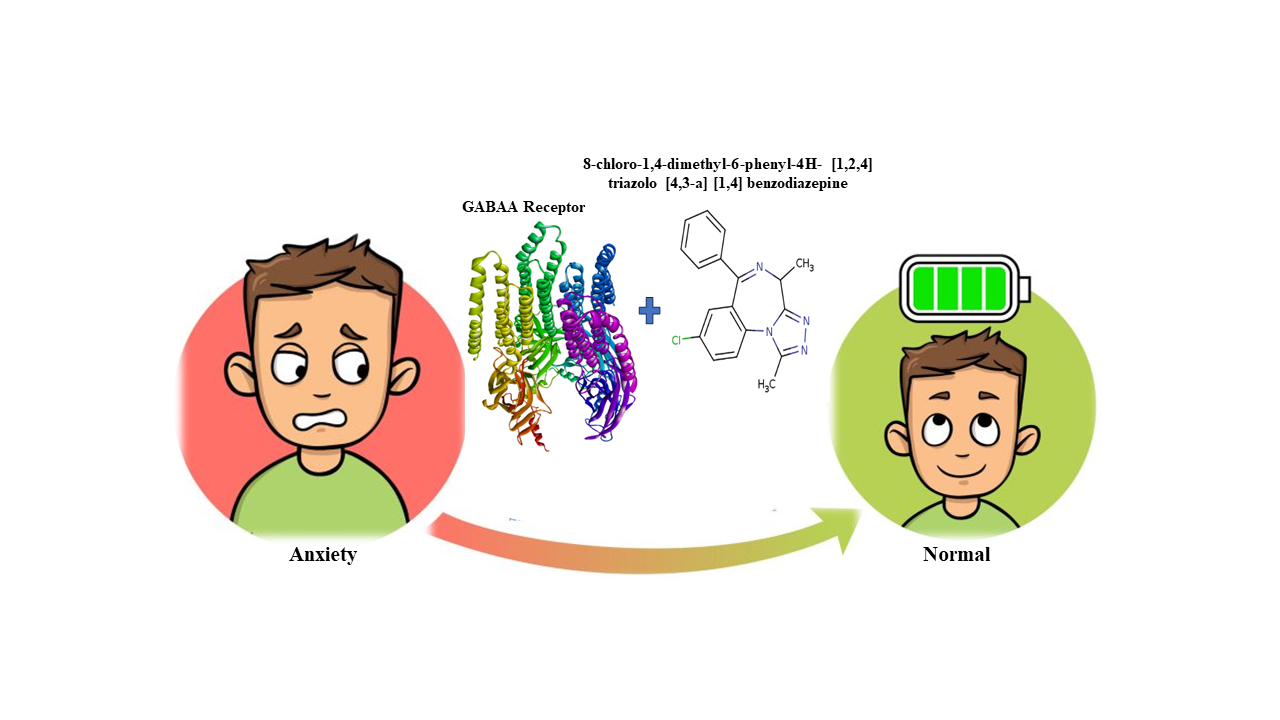
GABAA receptors exhibit permeability to the chloride ion-gated channel, and an increase in excitability disrupts the ion gradients, hence contributing to the development of anxiety-related disorders. This study aims to repurpose potent inhibitors of alprazolam analogs, which were obtained from the PubChem database. These ligands are being investigated for their binding ability to the GABAA receptor. We employed molecular docking through Autodock vina V.4.2 software. The Swiss ADME server was utilized to assess the drug-likeness of the ligands. MDS was conducted using the iMODS platform. Compounds A3, A8, and A9 exhibited a notable binding score range of -8.0 to -8.4 kcal/mol-1 with GABAA protein. The drug-likeness analysis revealed that 3 ligands had compliance with Lipinski's RO5. Moreover, the A8 compound can traverse the BBB. In contrast, the A3 and A9 ligands remain localized in the GI region. The MDS of the GABAA receptor with the A8 molecule exhibited higher stability than alprazolam. The current investigation unveiled a highly effective antagonist of GABAA receptors, specifically A8 - 8-chloro-1,4-dimethyl-6-phenyl-4H- [1,2,4] triazolo [4,3-a] [1,4] benzodiazepine. This compound holds potential for future wet-lab experiments, perhaps leading to its utilization in therapeutic applications as an anxiolytic medication.
References
Aldossari, R. M., Ali, A., Rehman, M. U., Rashid, S., & Ahmad, S. B. (2023). Computational approaches for identification of potential plant bioactives as novel G6PD inhibitors using advanced tools and databases. Molecules, 28(7), 3018. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28073018 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28073018
Azad, A. K., Praveen, M., Sulaiman, W., & Ma, B. W. (2024a). Assessment of anticancer properties of Plumbago zeylanica. In: Advances in medical diagnosis, treatment, and care (AMDTC) book series, (91-121 p). https://doi.org/10.4018/979-8-3693-1646-7.ch004 DOI: https://doi.org/10.4018/979-8-3693-1646-7.ch004
Bhattacharya, K., Bordoloi, R., Chanu, N. R., Kalita, R., Sahariah, B. J., & Bhattacharjee, A. (2022). In silico discovery of 3 novel quercetin derivatives against papain-like protease, spike protein, and 3C-like protease of SARS-CoV-2. Journal of Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology, 20(1), 43. https://doi.org/10.1186/s43141-022-00314-7 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s43141-022-00314-7
Bloom, F. E., & Iversen, L. L. (1971). Localizing 3H-GABA in nerve terminals of rat cerebral cortex by electron microscopic autoradiography. Nature, 229, 628-630. https://doi.org/10.1038/229628a0 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/229628a0
Brioni, J. D., Nagahara, A. H., & McGaugh, J. L. (1986). Involvement of the amygdala GABAergic system in the modulation of memory storage. Brain Research, 487(1), 105-112. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-8993(89)90945-1 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-8993(89)90945-1
Chua, P., Krams, M., Toni, I., Passingham, R., & Dolan, R. (1999). A functional anatomy of anticipatory anxiety. NeuroImage, 9(6), 563-571. https:// doi.org/10.1006/nimg.1999.0407 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1006/nimg.1999.0407
Daina, A., Michielin, O., & Zoete, V. (2017). SwissADME: a free web tool to evaluate pharmacokinetics, drug-likeness and medicinal chemistry friendliness of small molecules. Science Reports, 7, 42717. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep42717 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/srep42717
Daina, A., & Zoete, V. (2016). A BOILED-Egg to predict gastrointestinal absorption and brain penetration of small molecules. ChemMedChem, 11(11), 1117-1121. https://doi.org/10.1002/cmdc.201600182 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/cmdc.201600182
Erdõ, S. L., Varga, B., Horváth, E. (1985). Effect of local GABA administration on rat ovarian blood flow, and on progesterone and estradiol secretion. European Journal of Pharmacology, 111(3), 397-400. https://doi.org/10.1016/0014-2999(85)90650-8 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0014-2999(85)90650-8
Ertl, P., Rohde, B., & Selzer, P. (2000). Fast calculation of molecular polar surface area as a sum of fragment-based contributions and its application to the prediction of drug transport properties. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 43(20), 3714-3717. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm000942e DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/jm000942e
Gee, K. W., Chang, W. C., Brinton, R. E., & McEwen, B. S. (1987). GABA-dependent modulation of the Cl- ionophore by steroids in rat brain. European Journal of Pharmacology, 136(3), 419-442. https://doi.org/10.1016/0014-2999(87)90317-7 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0014-2999(87)90317-7
Goodsell, D. S., Morris, G. M., & Olson, A. J. (1996). Automated docking of flexible ligands: Applications of AutoDock. Journal of Molecular Recognition, 9(1), 1-5. https://doi.org/10.1002/(sici)1099-1352(199601)9:1%3C1::aid-jmr241%3E3.0.co;2-6 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1099-1352(199601)9:1<1::AID-JMR241>3.0.CO;2-6
Granger, R. E., Campbell, E. L., & Johnston, G. A. R. (2005). (+)- and (-)-borneol: Efficacious positive modulators of GABA action at human recombinant α1β2γ2L GABAA receptors. Biochemical Pharmacology, 69(7), 1011-1111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2005.01.002 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2005.01.002
Griffin, C. E., Kaye, A. M., Bueno, F. R., & Kaye, A. D. (2013). Benzodiazepine pharmacology and central nervous system-mediated effects. The Ochsner Journal, 13(2), 214-223.
Hester, J. B., Rudzik, A. D., & VonVoigtlander, P. F. (1980). 8-Chloro-1-Methyl-6-Phenyl-4H-s-Triazolo[4,3-a][1,4] Benzodiazepines with Substituents at C-4. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 23, 643-64. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm00180a012 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/jm00180a012
Irvine, J. D., Takahashi, L., Lockhart, K., Tolan, J. W., Selick, H. E., & Grove, J. R. (1999). MDCK (Madin-Darby canine kidney) cells: A tool for membrane permeability screening. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 88(1), 28-33. https://doi.org/10.1021/js9803205 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/js9803205
Junior, F. J. B., Scotti, L., Ishiki, H., Botelho, S. P. S., Silva, M. S., & Scotti, M. T. (2015). Benzo- and Thienobenzo- Diazepines: multi-target drugs for CNS disorders. Mini Reviews in Medicinal Chemistry, 15(8), 630-647. https://doi.org/10.2174/1389557515666150219125030 DOI: https://doi.org/10.2174/1389557515666150219125030
Kent, J. M., Mathew, S. J., & Gorman, J. M. (2002). Molecular targets in the treatment of anxiety. Bio Psychiatry 52, 1008-1030. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0006-3223(02)01672-4 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0006-3223(02)01672-4
Kim, S., Thiessen, P. A., Bolton, E. E., Chen, J., Fu, G., Gindulyte, A., Han, L., He, J., He, S., Shoemaker, B. A.(2016). PubChem substance and compound databases. Nucleic Acids Research, 44(D1), 1202-1213 https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkv951 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkv951
Lipinski, C. A. (2000). Drug-like properties and the causes of poor solubility and poor permeability. Journal of Pharmacological and Toxicological Methods, 44(1), 235-249. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1056-8719(00)00107-6 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1056-8719(00)00107-6
Lipinski, C. A. (2004). Lead- and drug-like compounds: The rule-of-five revolution. Drug Discovery Today: Technology, 1, 337-341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ddtec.2004.11.007 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ddtec.2004.11.007
Nayeem, N., Green, T. P., Martin, I. L., & Barnard, E. A. (1994). Quaternary structure of the native GABAA receptor determined by electron microscopic image analysis. Journal of Neurochemistry, 62(2), 815-818. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1471-4159.1994.62020815.x DOI: https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1471-4159.1994.62020815.x
O’Boyle, N. M., Banck, M., James, C. A., Morley, C., Vandermeersch, T., & Hutchison, G. R. (2011). Open Babel: An Open chemical toolbox. Journal of Cheminformatics, 3, 33. https://doi.org/10.1186/1758-2946-3-33 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1758-2946-3-33
Pokharkar, O., Lakshmanan, H., Zyryanov, G., & Tsurkan, M. (2022). In silico evaluation of antifungal compounds from marine sponges against COVID-19-associated mucormycosis. Marine Drugs, 20(3), 215. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20030215 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/md20030215
Praveen, M., & Morales-Bayuelo, A. (2023). Drug designing against VP4, VP7 and NSP4 of rotavirus proteins – Insilico studies, Moroccan Journal of Chemistry, 14(6), 729-741. https://doi.org/10.48317/IMIST.PRSM/morjchem-v11i3.40088
Praveen, M., Ullah, I., Buendia, R., Khan, I. A., Sayed, M. G., Kabir, R., Bhat, M., & Yaseen, M. (2024). Exploring Potentilla nepalensis phytoconstituents: Integrated strategies of network pharmacology, molecular docking, dynamic simulations, and MMGBSA analysis for cancer therapeutic targets discovery. Pharmaceuticals, 17(1), 134. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17010134 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17010134
Praveen, M. (2024b). Characterizing the West Nile Virus’s polyprotein from nucleotide sequence to protein structure – Computational tools. Journal of Taibah University Medical Sciences. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtumed.2024.01.001 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtumed.2024.01.001
Praveen, M. (2024c). Multi-epitope-based vaccine designing against Junín virus glycoprotein: immunoinformatics approach. Future Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 10(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s43094-024-00602-8 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s43094-024-00602-8
Reiman, E. M., Fusselman, M. J., Fox, P. T., & Raichle, M. E. (1979). Neuroanatomical correlates of anticipatory anxiety. Science, 243(4894), 1071-1074. https://doi.org/10.1002/da.22977 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.2784226
Renard, S., Olivier, A., Granger, P., Sevrin, M., George, P., & Bernard, F. (1999). Structural elements of the γ-aminobutyric acid type A receptor conferring subtype selectivity for benzodiazepine site ligands. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 274(19), 13370-13374. https://www.jbc.org/article/S0021-9258(18)36888-1/fulltext DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.274.19.13370
Riba, J., Rodríguez-Fornells, A., Urbano, G., Morte, A., Antonijoan, R., & Barbanoj, M. J. (2001). Differential effects of alprazolam on the baseline and fear-potentiated startle reflex in humans: a dose-response study. Psychopharmacology, 157, 358-367. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002130100816 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002130100816
Saano, V. (1987). GABA-benzodiazepine receptor complex and drug actions. Medical Biology, 65(2), 167-173.
Schwartz, R. D. (1998). The GABAa receptor-gated ion channel: Biochemical and pharmacological studies of structure and function. Biochemical Pharmacology, 37(18), 3369-3375. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-2952(88)90684-3 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-2952(88)90684-3
Trott, O., Olson, A. J. (2009). AutoDock Vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. Journal of Computational Chemistry, 31(2), 455-461. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcc.21334 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/jcc.21334
Vijayan, R. S. K., Bhattacharyya, D., Ghoshal, N. (2012). Deciphering the binding mode of Zolpidem to GABA A α 1 receptor - Insights from molecular dynamics simulation. Journal of Molecular Modeling, 18, 1345-1354. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-011-1142-0
Wade, R. C., & Goodford, P. J. (1989). The role of hydrogen-bonds in drug binding. Progress in Clinical and Biology Research, 289, 433-444.
Zaib, S., Akram, F., Waris, W., Liaqat, S. T., Zaib, Z., Khan, I., Dera, A. A., Pashameah, R. A., Alzahrani, E., & Farouk, A. E. (2022). Computational approaches for innovative anti-viral drug discovery using Orthosiphon aristatus blume miq against dengue virus. Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics, 27(18), 1-13. https://doi.org/10.1080/07391102.2022.2137238 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/07391102.2022.2137238
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Mallari Praveen, Vijay Paramanik

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
1) Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
2) Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.
3) Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work.


