Precision and innovation: Carbon dioxide laser excision of ranula
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14295/bjs.v3i9.640Keywords:
mucocele, sublingual gland, floor of mouth, carbon dioxide laser, surgical excisionAbstract
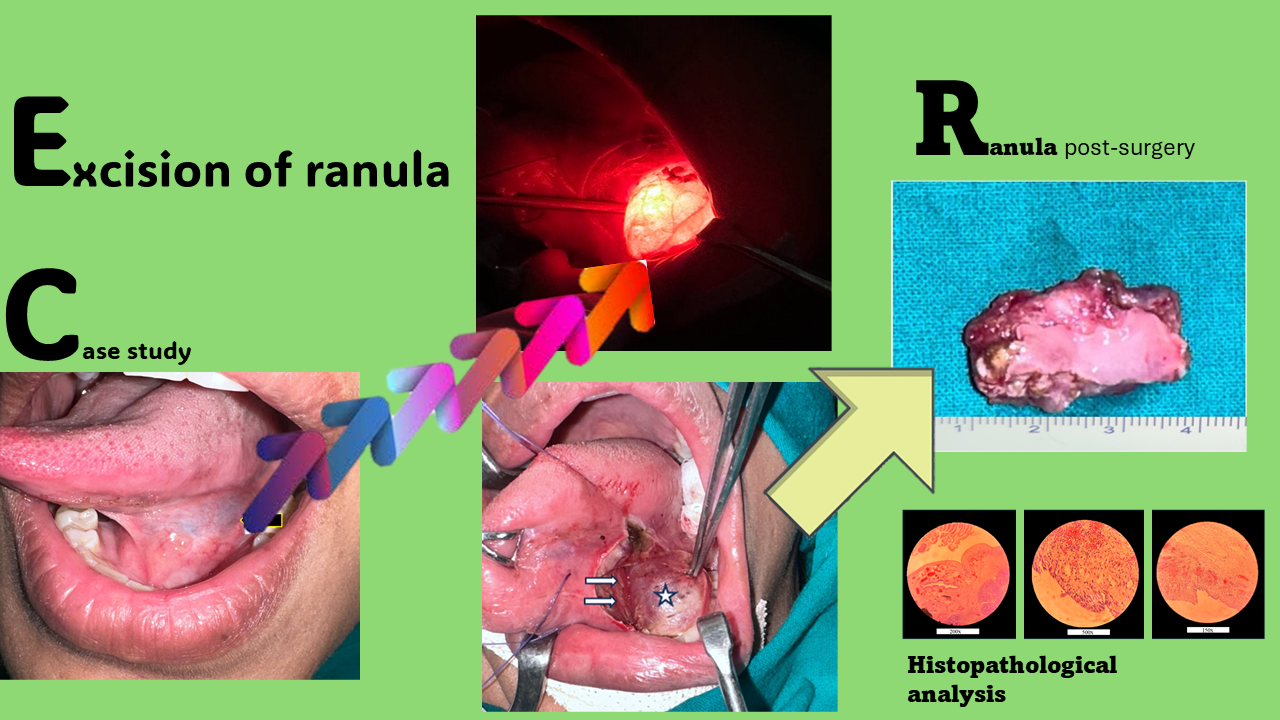
A ranula is a relatively uncommon condition characterized by the formation of a mucus-filled cyst within the floor of the mouth. This benign lesion typically originates from a blocked or damaged sublingual salivary gland duct, accumulating saliva in a localized cyst-like structure. Aspiration of cystic fluid, sclerotherapy, marsupialization, incision and drainage, excision of the ranula alone, excision of the sublingual gland with or without ranula, laser excision, and ranula vaporization are just a few of the suggested therapies for ranula. The outcomes of the varied treatments have been inconsistent. Most surgeons concur that the sublingual gland must be removed from the ranula. The authors provide a case report on carbon dioxide laser treatment for ranula, as well as a literature review. According to the authors' experience and literature, carbon dioxide laser excision of ranula is a safe procedure with minimum recurrence.
References
Abdul-Aziz, D., & Adil, E. (2015). Ranula excision. Operative Techniques in Otolaryngology – Head and Neck Surgery, 26(1), 21-27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otot.2015.01.005 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otot.2015.01.005
Asnaashari, M., Mohebi, S., & Paymanpour, P. (2011). Pain reduction using low level laser irradiation in single-visit endodontic treatment. Journal of Lasers in Medicinal Sciences, 2(04), 139-143.
Asnaashari, M., & Zadsirjan, S. (2014). Application of laser in oral surgery. Journal of Lasers in Medicinal Sciences, 5(03), 97-107. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25653807
Barak, S., Horowitz, I., Katz, J., & Kaplan, I. (1991). Experiences with the CO2 laser in the surgical treatment of intra-oral salivary gland pathology. Journal of Clinical Laser Medicine & Surgery, 9(4), 297. https://doi.org/10.1089/clm.1991.9.295 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1089/clm.1991.9.295
Basu, M. K., Frame, J. W., & Rhys, P. H. (1988). Wound healing following partial glossectomy using the CO2 laser, diathermy and scalpel: a histological study in rats. The Journal of Laryngology and Otology, 102(4), 322-327. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022215100104852 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022215100104852
Bhaskar, S. N., Bolden, T. E., & Weinmann, J. P. (1956). Pathogenesis of mucoceles. Journal of Dental Research, 35(06), 863-874. https://doi.org/10.1177/00220345560350060601 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/00220345560350060601
Bronstein, S. L., & Clark, M. S. (1984). Sublingual gland salivary fistula and sialocele. Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology, 57(4), 357-361. https://doi.org/10.1016/0030-4220(84)90149-X DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0030-4220(84)90149-X
Catone, G. A. (1997). Laser applications in oral and maxillofacial surgery. Saunders, W. B., Philadelphia, 307 p. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1097/00008505-199700630-00026
Crysdale, W. S., Mendelsohn, J. D., & Conley, S. (1988). Ranulas–mucoceles of the oral cavity: experience in 26 children. The Laryngoscope, 98(3), 296-298. https://doi.org/10.1288/00005537-198803000-00011 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1288/00005537-198803000-00011
Curtin, H. D. (2007). Imaging of the Salivary gland. In: Myers Eugene, N., Ferris Robert, L. (eds) Myers’ salivary gland disorders. Springer, Berlin, 17-31 p. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-47072-4_2
Davison, M. J., Morton, R. P., McIvor, N. P. (1998). Plunging ranula: Clinical observations. Journal of the Sciences and Specialties of the Head Neck, 20(1), 63-68. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-0347(199801)20:1%3C63::AID-HED10%3E3.0.CO;2-Q DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-0347(199801)20:1<63::AID-HED10>3.3.CO;2-D
Duncavage, J. A., & Ossoff, R. H. (1986). Use of the CO2 laser for malignant disease of the oral cavity. Laser in Surgery and Medicine, 6(5), 442-444. https://doi.org/10.1002/lsm.1900060504 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/lsm.1900060504
Fisher, S. E., & Frame, J. W. (1984). The effect of the CO2 surgical laser on oral tissues. British Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, 22(6), 414-418. https://doi.org/10.1016/0266-4356(84)90048-2 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0266-4356(84)90048-2
Frame, J. W. (1985). Removal of soft tissue pathology with the CO2 laser. Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, 43(11), 850-855. https://doi.org/10.1016/0278-2391(85)90221-6 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0278-2391(85)90221-6
Gáspár, L., & Szabo, G. (1990). Manifestations of the advantages and disadvantages of using the CO2 laser in oral surgery. Journal of Clinical Laser Medicine & Surgery, 8(1), 39-43. PMID: 10148946
Gáspár, L., Sudár, F., Tóth, J., & Madarász, B. (2009). Oral lesions induced by scalpel. electrocautety, and CO2 laser compared with light. scanning and electron microscopy. Journal of Clinical Laser Medicine & Surgery, 9(5), 349. https://doi.org/10.1089/clm.1991.9.349 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1089/clm.1991.9.349
Golden, B., Drake, A. F., & Talavera, F., & Roland, P. S. (2016). Ranulas and plunging ranulas. Medscape Last updated March 28. Available in: https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/847589-overview Access in: July 20, 2024
Gontarz, M., Bargiel, J., Gąsiorowski, K., Marecik, T., Szczurowski, P., Zapała, J., Gałązka, K., & Wyszyńska-Pawelec, G. (2023). Surgical treatment of sublingual gland ranulas. International Archives of Otorhinolaryngology, 27(2), e296-e301. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0042-1744166 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0042-1744166
Harrison, J. D. (2010). Modern management and pathophysiology of ranula: Literature review. Journal of the Sciences and Specialties of the Head Neck, 32(10), 1310-1320. https://doi.org/10.1002/hed.21326 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/hed.21326
Koch, M., Mantsopoulus, K., Leibl, V., Müller, S., Iro, H., & Sievert, M. (2022). Ultrasound in the diagnosis and differential diagnosis of enoral and plunging ranula: a detailed and comparative analysis. Journal of Ultrasound, 26(2), 487-495. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40477-022-00743-7 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40477-022-00743-7
Kolong, D., Iduh, A., Chukwu, I., Mugu, J., Nhu, S., & Augustine, S. (2017). Ranula: Current concept of pathophysiologic basis and surgical management options. World Journal of Surgery, 41, 1476-1481. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-017-3901-2 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-017-3901-2
Langlois, N. E., & Kolhe, P. (1992). Plunging ranula - A case report and a literature review. Human Pathology, 23(11), 1306-1308. https://doi.org/10.1016/0046-8177(92)90300-R DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0046-8177(92)90300-R
Morton, R. P., & Bartley, J. R. (1995) Simple sublingual ranulas: pathogenesis and management. Journal of Otolaryngology, 24(4), 253-254. PMID: 8551539
Morton, R. P., Ahmad, Z., & Jain, P. (2010). Plunging ranula: congenital or acquired? Otolaryngology Head Neck Surgery, 142(1), 104-107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otohns.2009.10.014 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otohns.2009.10.014
Morton, R. P. (2018). Surgical management of ranula revisited. World Journal of Surgery, 42, 3062-3063. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-018-4666-y DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-018-4666-y
Niccoli-Filho, W., & Morosolli, A. R. C. (2003). CO2 laser treatment of actinic cheilitis associated with squamous-cell carcinoma of lower lip. Journal of Oral Laser Applications, 3(4), 251-253.
Patel, M. R., Deal, A. M., & Shockley, W. W. (2009) Oral and plunging ranulas: what is the most effective treatment? Laryngoscope, 119(8), 1501-1509. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.20291 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.20291
Pogel, M. A., McCracken, K. J., & Daniels, T. E. (1990). Histologic evaluation of the width of soft tissue necrosis adjacent to carbon dioxide laser incisions. Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology, 70(5), 564-568. https://doi.org/10.1016/0030-4220(90)90397-B DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0030-4220(90)90397-B
Rho, M. H., Kim, D. W., Kwon, J. S., (2006). OK-432 sclerotherapy of plunging ranula in 21 patients: It can be a substitute for surgery. American Journal of Neuroradiology, 27(5), 1090-1095. https://www.ajnr.org/content/27/5/1090.short
Rosen, D., Wirtschafter, A., Rao, V. M., Wilcox, T. O. (1998). Dermoid cyst of the lateral neck: A case report and literature review. Ear, Nose & Throat Journal, 77(125), 129-132. https://doi.org/10.1177/014556139807700212 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/014556139807700212
Sheldon, M., Shlomo, B., & Isack, H. (1994). Carbon dioxide laser excision and vaporization of nonplunging ranulas: A comparison of two treatment protocols. Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, 52(4), 370-372. https://doi.org/10.1016/0278-2391(94)90439-1 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0278-2391(94)90439-1
Suzanne, G. (1887). Recherches anatomiques sur le plancher de la bouche, avec études anatomique et pathogenique sur la grenouillette commune ou sublinguale. Archives de Physiologie Normale et Pathologique, 10, 141-197.
Tavill, M. A., Poje, C. P., Wetmare, R. F., & Faro, S. H. (1995). Plunging ranulas in children. Annals of Otology, Rhinology & Laryngology, 104(5), 405-408. https://doi.org/10.1177/000348949510400512 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/000348949510400512
Thompson, J. E. (1920). The relationship between ranula and branchio-genetic cysts. Annals of Surgery, 72(2), 164-176. https://doi.org/10.1097%2F00000658-192008000-00008 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1097/00000658-192008000-00008
Turetschek, K., Hospdka, H., & Steiner, E. (1995). Case report: epidermoid cyst of the floor of the mouth: diagnostic imaging by sonography, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. The British Journal of Radiology, 68(806), 205-207. https://doi.org/10.1259/0007-1285-68-806-205 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1259/0007-1285-68-806-205
Vogl, T. J., Steger, W., Ihrler, S., Ferrera, P., & Grevers, G. (1993). Cystic masses in the floor of the mouth: value of MR imaging in planning surgery. AJR American Journal of Roentgenology, 161(1), 183-186. https://doi.org/10.2214/ajr.161.1.8517299 DOI: https://doi.org/10.2214/ajr.161.1.8517299
von Hippel, R. (1897). Ueber Bau und Wesen der Ranula. Archiv für klinische Chirurgie, 55, 164-193.
White, D. K., Davidson, H. C., Harnsberger, H. R., Haller, J., Kamya, A. (2001). Accessory salivary tissue in the mylohyoid boutonnière: A clinical and
radiologic pseudolesion of the oral cavity. American Journal of Neuroradiology, 22(2), 406-412. https://www.ajnr.org/content/22/2/406.short
Yang, Y., & Hong, K. (2014). Surgical results of the intraoral approach for plunging ranula. Acta Oto-Laryngologica, 134(2), 201-205. https://doi.org/10.3109/00016489.2013.83148 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3109/00016489.2013.831481
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Pankaj Goyal, Kishan Kumawat, Manisha Chouhan, Chandrani Chatterjee, Nirupama Kothari

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
1) Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
2) Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.
3) Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work.


