Toxic effect of elements on the germination and initial development of barley seeds (Hordeum vulgare L.)
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14295/bjs.v3i2.520Keywords:
toxicity, heavy metals, Poaceae family, barley, agricultural cultivar, toxicity tolerant plantsAbstract
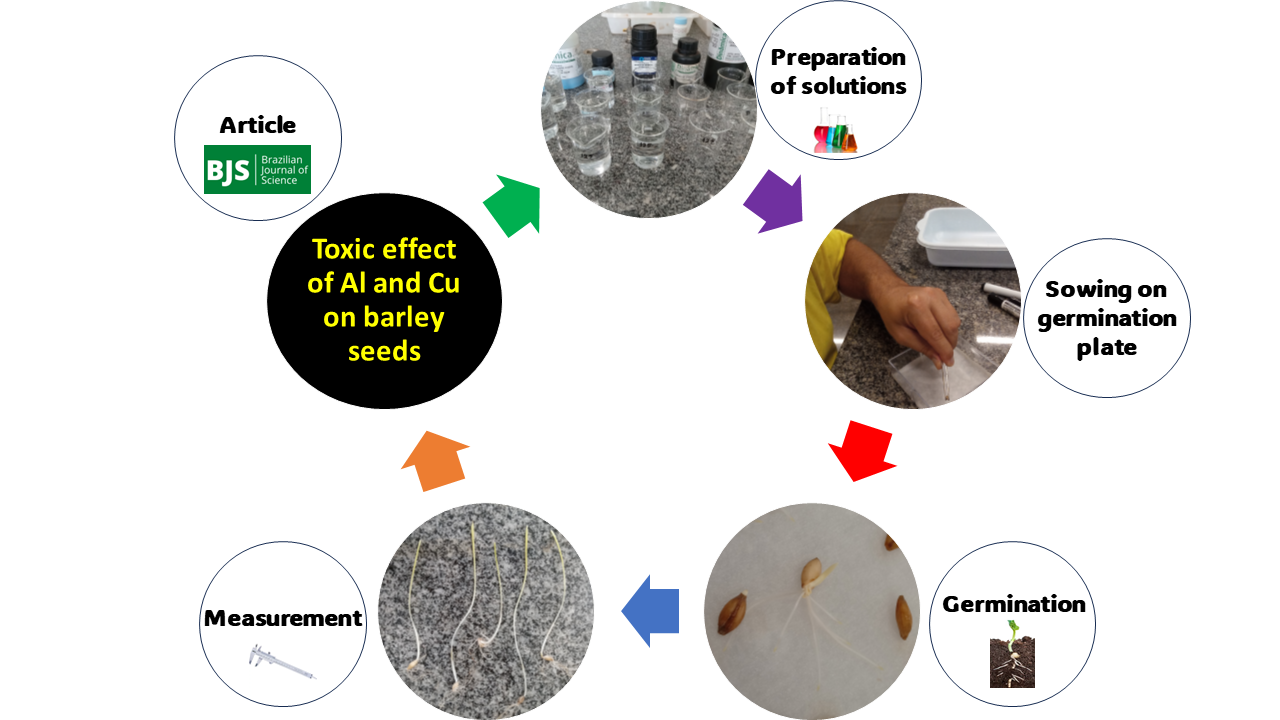
Barley (Hordeum vulgare) is an agricultural vegetable from the Poaceae family used in food and beer production. The study aimed to evaluate the toxic effect of Aluminum (Al) and Copper (Cu) on germination and initial development in barley seeds cultivar KWS Irina. Different concentrations (0, 35, 85 and 125 mg L-1) of aqueous solution of Al and Cu were produced from their chlorides. The toxicity experiment was carried out in a germination box maintained in a germination chamber with a 12-h photoperiod. After 15 days of germination, the seedlings were measured using a millimetric ruler (cm) where they were evaluated for plant length, root length, and fresh and dry mass of plant and root determined on a digital analytical scale (g). Barley seedlings cultivar KWS Irina demonstrated to be intolerant to concentrations of the toxic elements Al and Cu in all plant parameters analyzed, except for plant dry mass. Future studies should be carried out comparing the initial and reproductive development of this barley cultivar in terms of the presence and absence of toxic elements.
References
Ahmad, Z., Khan, S. M., Page, S. E., Balzter, H., Ullah, A., Ali, S., Jehangir, S., Ejaz, U., Afza, R., & Razzaq, A. (2023). Environmental sustainability and resilience in a polluted ecosystem via phytoremediation of heavy metals and plant physiological adaptations. Journal of Cleaner Production, 385, 135733. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.135733 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.135733
Alves, C. Z., Silva, J. B., & Cândido, A. C. S. (2015). Metodologia para a condução do teste de germinação em sementes de goiaba. Revista Ciência Agronômica, 46(3), 615-621. https://doi.org/10.5935/1806-6690.20150045 DOI: https://doi.org/10.5935/1806-6690.20150045
Augusto, A. S., Bertoli, A. C., Cannata, M. G., Carvalho, R., & Bastos, A. R. R. (2014). Bioacumulação de metais pesados em Brassica juncea: Relação de Toxicidade com elementos essenciais. Revista Virtual de Química, 6(5), 1221-1236. http://dx.doi.org/10.5935/1984-6835.20140080 DOI: https://doi.org/10.5935/1984-6835.20140080
Braccini, M. C. L., Martinez, H. E. P., & Braccini, A. L. (2000). Avaliação do pH da rizosfera de genótipos de café em resposta à toxidez de alumínio no solo. Bragantia, 59(1), 83-88. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0006-87052000000100013 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1590/S0006-87052000000100013
Cakir, E., Arici, M., & Durak, M. Z. (2021). Effect of starter culture sourdough prepared with Lactobacilli and Saccharomyces cerevisiae on the quality of hull-less barley-wheat bread. LWT, 152, 112230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2021.112230 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2021.112230
Chatterjee, J. & Chatterjee, C. (2000). Phytotoxicity of cobalt, chromium and copper in cauliflower. Environmental Pollution, 109(1), 69-74, 2000. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0269-7491(99)00238-9
Cichelero, L. H., Silva, D. M., Bohrer, R. E. G., Silva, D. A. A., Redin, M., Souza, E. L., Guerra, D., Vasconcelos, M. C., & Lanzanova, M. E. (2023). Doses de dejetos líquidos de suínos e seu efeito na germinação de sementes de soja, trigo e milho. Investigación Agraria, 25(1), 11-18. https://doi.org/10.18004/investig.agrar.2023.junio.2501724 DOI: https://doi.org/10.18004/investig.agrar.2023.junio.2501724
Cunha, G. R., Dalmago, G. A., Estefanel, V., Pasinato, A., & Moreira, M. B. (2001). El Niño – Ocilação do Sul e seus impactos sobre a cultura de cevada no Brasil. Revista Brasileira de Agrometeorologia, 9(1), 137-145.
Ellwanger, J. H., & Chies, J. A. B. (2023). Brazil’s heavy metal pollution harms humans and ecosystems. Science in One Health, 2, 100019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soh.2023.100019 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soh.2023.100019
Ferreira, D. F. (2019). Sisvar: A computer analysis system to fixed effects split plot type designs. Brazilian Journal of Biometrics, 37(4), 529-535. https://doi.org/10.28951/rbb.v37i4.450 DOI: https://doi.org/10.28951/rbb.v37i4.450
Gabriel, L., Volpe, M. C., Cristiano, G. A., Neves, V. D. D., Souza, D. S. S., Ramos, J. L., Portela, A. L. R., Dias, A. B., Villa, F. B., Godoy, G. B., Godoi, I. R. G., Monteiro, J. O. F., Sebastiani, R., & Pelegrini, R. T. (2019). Estudos da toxicidade do alumínio em valores de pH 7,0 e 7,5 para Brassica oleracea L. e Raphanus sativus L. Brazilian Journal of Biosystems Engineering, 13(4), 312-323. https://doi.org/10.18011/bioeng2019v13n4p312-323 DOI: https://doi.org/10.18011/bioeng2019v13n4p312-323
Galon, L., Tironi, S. P., Rocha, P. R. R., Concenço. G., Silva, A. F., Vargas, L., Silva, A. A., Ferreira, E. A., Minella, E., Soares, E. R., & Ferreira, F. A. (2011). Habilidade competitive de cultivares de cevada convivendo com azevém. Planta Daninha, 29(4), 771-781. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-83582011000400007 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-83582011000400007
Gentelina, W. C., & Soster, M. T. B. (2015). Efeito do silício na germinação e desenvolvimento inicial de cevada e trigos aplicados na sementes. In: Anais do 30ª Reunião Nacional de Pesquisa de Cevada, Passo Fundo, 14 a 14 de Abril, Embrapa, Brasília, DF, 164-172.
Gonçalves, H. M., Borges, J. D., & Silva, M. A. S. (2009). Acúmulo de metais pesados e enxofre no solo em áreas de Influência de canais de vinhaça de fertirrigação. Bioscience Journal, 25(6), 66-74.
Guo, T. R., Zhang, G. P., & Zhang, Y. H. (2007). Physiological changes in barley plants under combined toxicity of aluminum, copper and cadmium. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 57, 182-188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2007.01.013 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2007.01.013
Leite, P. R. V., & Zampieron, J. V. (2012). Avaliação da cultura de feijão (Phaseolus vulgaris cv carioquinha) em solo contaminados por metais pesados, utilizando técnicas de microscopia eletrônica de varredura e espectrometria por dispersão de energía. Revista Agrogeoambiental, 4(3), 1-8. https://doi.org/10.18406/2316-1817v4n32012471 DOI: https://doi.org/10.18406/2316-1817v4n32012471
Li, B., Ma, Y., McLaughlin, M. J., Kirby, J. K., Cozens, G., & Liu, J. (2010). Influences of soil properties and leaching on copper toxicity to barley root elongation. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 29(4), 835-842. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.108 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.108
Lock, L., Criel, P., De Schamphelaere, K. A. C., Van Eeckhout, H., & Janssen, C. R. (). Influence of calcium, magnesium, sodium, potassium and pH on copper toxicity to barley (Hordeum vulgare). Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 68(2), 299-304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2006.11.014 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2006.11.014
Mori, C., & Minella, E. (2012). Aspectos econômicos e conjunturais da cultura da cevada. Embrapa Trigo, Passo Fundo, RS, Brasil, Documentos Online, 139, 28 p. http://www.cnpt.embrapa.br/biblio/do/p_do139.htm
Ozygit, I. I., Abakirova, A., Hocaoglu-Ozygit, A., Kurmanbekova, G.; Chekirov, K., Yalcin, B., Yalcin, I. E. (2021). Cadmium stress in barley seedlings: Accumulation, growth, anatomy and physiology. International Journal of Life Sciences and Biotechnology, 4(2), 204-223. 10.38001/ijlsb.833611 DOI: https://doi.org/10.38001/ijlsb.833611
Ramalho, J. F. G. P., & Sobrinho, N. M. B. A. (2001). Metais pesados em solos cultivadas com cana-de-açúcar pelo uso de resíduos agroindustriais. Flor@m Floresta e Ambiente, 8(1), 120-129. http://www.floram.periodikos.com.br/article/588e21f8e710ab87018b45c5
Santos, V. D., Borba, L. B., Bresolin, S., Zarnot, M. S., Alemeida, A. R. F. (2018). Estudo comparative da secagem em leitos de jorro e fluidizado de sementes de cevada (Hordeum vulgare L.). Revista da Jornada da Pós-Graduação e Pesquisa – Congrega, 168-178. http://ediurcamp.urcamp.edu.br/index.php/rcjpgp/article/view/2812/1921
Souza, E. P., Silva, I. F., & Ferreira, L. E. (2011). Mecanismos de tolerância a estresses por metais pesados em plantas. Revista Brasileira de Agrociência, 17(2-4), 167-173. https://periodicos.ufpel.edu.br/index.php/CAST/article/view/2046
Stefanello, R., & Goergen, P. C. H. (2019). Toxicidade de alumínio na germinação de sementes de Cynara scolymus L.. Cultura Agronômica, 28(1), 42-49. https://doi.org/10.32929/2446-8355.2019v28n1p42-49 DOI: https://doi.org/10.32929/2446-8355.2019v28n1p42-49
Tsukamoto, T., Nakanishi, H., Kiyomiya, S (2006). Mn translocation in barley monitored using a positron-emeitting tracer imaging system. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 52(6), 717-725. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1747-0765.2006.00096.x
Wang, X., Ma, Y., Hua, L., McLaughlin, M. J. (2009). Identification of hydroxyl copper toxicity to barley (Hordeum vulgare) root elongation in solution culture. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 28(3), 662-667. https://doi.org/10.1897/07-641.1 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1897/07-641.1
Yang, Y., Wang, S., Zhao, C., Jiang, X., & Gao, D. (2024). Responses of non-structural carbohydrates and biomass in plant to heavy metal treatment. Science of the Total Environment, 909, 168559. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.168559 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.168559
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Ranyele Renata Leite, Antonio Carlos Pereira de Menezes Filho, Leandro Carlos, Porshia Sharma, Matheus Vinicius Abadia Ventura, Carlos Frederico de Souza Castro, Marconi Batista Teixeira, Frederico Antônio Loureiro Soares, Daniel Noe Coaguila Nuñez

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
1) Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
2) Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.
3) Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work.


