Phyto-assisted synthesis of Silver nanoparticles using Tinospora cordifolia leaf extract and their antibacterial activity: An ecofriendly approach
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14295/bjs.v3i2.501Keywords:
Silver nanoparticles (SNP), Tinospora cordifolia, characterization, antimicrobial activityAbstract
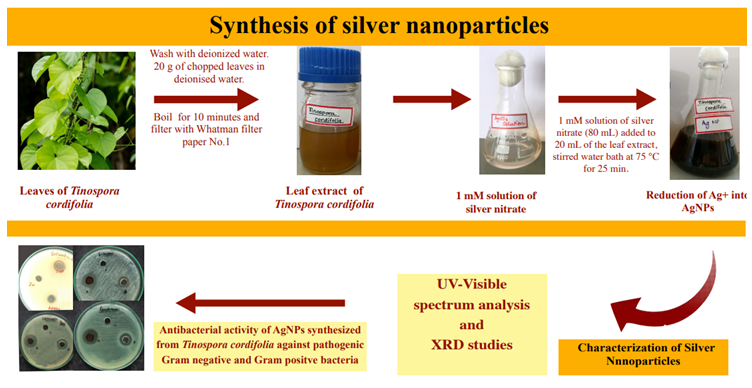
To meet the increasing demands for commercial nanoparticles new eco-friendly methods of synthesis are being discovered. Plant mediated synthesis of nanoparticles offers single step, easy extracellular synthesis of nanoparticles. We report the synthesis of antibacterial Silver nanoparticles using leaf extract of the medicinal plant, Tinospora cordifolia. The leaf extract was prepared by boiling chopped leaves of Tinospora cordifolia in deionized water for 10 min and filtering the mixture with Whatman filter paper No.1. The filtrate was used as a reducing agent and stabilising agent for AgNO3. On adding 1 mM solution of Silver nitrate to the leaf extract and stirring at 75 °C for 25 min, a change in colour from yellow-brown to brown-black specified the production of Silver nanoparticles. The formation of Silver nanoparticles was monitored by UV-visible spectroscopy and further characterization of the synthesized Silver nanoparticles was done by XRD studies. The antibacterial studies were performed on Gram negative and Gram positive pathogens, Salmonella typhi, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Enterobacter aerogenes and Staphylococcus aureus, by agar well diffusion method, on Mueller Hinton agar medium. The Silver nanoparticles synthesized from Tinospora cordifolia leaf extract were found to have antimicrobial activity against these Gram negative and Gram positive pathogenic bacteria.
References
Agarwal, S., & Priyadarshini, H. (2019). Assesment of anti- microbial activity of different concentrations of Tinospora cordifolia against Streptococcus mutans: an in-vitro study. Dental Research Journal, 16(1), 24-28. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6340217/ DOI: https://doi.org/10.4103/1735-3327.249556
Anuj, S. (2013). Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles by using Tinospora cordifolia stem powder, characterization and its antibacterial activity against antibiotics resistant bacteria. International Journal of Pharmacy Research and Technology, 3(2), 11-16. https://doi.org/10.31838/ijprt/03.02.03 DOI: https://doi.org/10.31838/ijprt/03.02.03
Ashraf, A., Zafar, S., Zahid, K., Shah, M. S., Al-Ghanim, K. A., Al-Misned, F., & Mahboob, S. (2019). Synthesis, characterization, and antibacterial potential of silver nanoparticles synthesized from Coriandrum sativum L, Journal of Infection and Public Health, 12(2), 275-281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiph.2018.11.002 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiph.2018.11.002
Babu, M. M. G., & Gunasekaran, P. (2009). Production and structural characterization of crystalline silver nanoparticles from Bacillus cereus isolate. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 74(1), 191-195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2009.07.016 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2009.07.016
Baptista, P. V., McCusker, M. P., Carvalho, A., Ferreira, D. A., Mohan, N. M., Martins, M., & Fernandes, A. R. (2018). Nano-strategies to fight multidrug resistant bacteria-a battle of the titans. Frontiers in Microbiology, 19, 1441. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.01441 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.01441
Barros, C. H. N., Fulaz, S., Stanisic, D., & Tasic, L. (2018). Biogenic nanosilver against multidrug-resistant bacteria (MDRB). Antibiotics, 7(3), 69. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics7030069 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics7030069
Begum, H. J., Ramamurthy, V., & Senthil Kumar, S. (2019). Study of synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles from Tinospora cordifolia. The Pharma Innovation Journal, 8(1), 612-615. https://www.thepharmajournal.com/archives/2019/vol8issue1/PartK/8-1-98-800.pdf
Daisy, P., & Saipriya, K. (2012). Biochemical analysis of Cassia fistula aqueous extract and phyto-chemically synthesized gold nanoparticles as hypoglycemic treatment for diabetes mellitus. International Journal of Nanomedicine, 7, 1189-1202. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S26650 DOI: https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S26650
Das, V. L., Thomas, R., Rintu, T., Varghese, E., Soniya, V., Mathew, J., & Radhakrishnan, E. K. (2014). Extracellular synthesis of silver nanoparticles by the Bacillus strain CS 11 isolated from industrialized area. 3Biotech, 4, 121-126. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-013-0130-8 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-013-0130-8
Dixit, M., & Shukla, P. (2020). Microbial nanotechnology for bioremediation of industrial wastewater. Frontiers in Microbiology, 11, 2411. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.590631 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.590631
Duraipandiyan, V., Ignacimuthu, S., Balakrishna, K., & Al-Harbi, N. A. (2012). Anti-microbial activity of Tinospora cordifolia: An ethnomedicinal plant. Asian Journal of Traditional Medicine, 7(2), 59-65. http://asianjtm.syphu.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract224.shtml
Elbeshehy, E. K. F., Elazzazy, A. M., & Aggelis, G. (2015). Silver nanoparticles synthesis mediated by new isolates of Bacillus spp., nanoparticle characterization and their activity against Bean Yellow Mosaic Virus and human pathogens. Frontiers in Microbiology, 1(6), 453. https://doi.org/10.3389%2Ffmicb.2015.00453 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2015.00453
Jain, K., Patel, A., Pardhi, V., & Flora, S. (2021). Nanotechnology in wastewater management: A new paradigm towards wastewater treatment. Molecules, 26(6), 1797. https://doi.org/10.3390%2Fmolecules26061797 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26061797
Jain, N., Bhargava, A., Majumdar, S., Tarafdar, J. C., & Panwar, J. (2011). Extracellular biosynthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles using Aspergillus flavus NJP08: A mechanism perspective. Nanoscale, 3(2), 635-641. https://doi.org/10.1039/C0NR00656D DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/C0NR00656D
Jayaseelan, C., Rahuman, A. A., Rajakumar, G., Kirthi, A. V., Santhoshkumar, T., & Marimuthu, S. (2011). Synthesis of pediculocidal and larvicidal silver nanoparticles by leaf extract from heart leaf moon seed plant Tinospora cordifolia Miers. Parasitology Research, 109, 185-194. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-010-2242-y DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-010-2242-y
Jha, A. K,. & Prasad, K. (2010). Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using cycas leaf. International Journal of Green Nanotechnology: Physics and Chemistry, 1(2), 110-117. https://doi.org/10.1080/19430871003684572 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/19430871003684572
Khan, I., Saeed, K., & Khan, I. (2019). Nanoparticles: Properties, applications and toxicities. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 12(7), 908-931. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2017.05.011 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2017.05.011
Mekky, A. E., Farrag, A., Ahmed, A. A., & Sofy, A. R. (2021). Preparation of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Aspergillus niger as antimicrobial and anticancer agents. Journal of Pure and Applied Microbiology, 15(3), 1547-1566. https://doi.org/10.22207/JPAM.15.3.49 DOI: https://doi.org/10.22207/JPAM.15.3.49
Mukherjee, P. K., Banerjee, S., Das Gupta, B., & Kar, A. (2022). Chapter 1 - Evidence-based validation of herbal medicine: Translational approach. In: Evidence-based validation of herbal medicine (Second Edition), Elsevier: 1-41. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-323-85542-6.00025-1. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-323-85542-6.00025-1
Narayanaswamy, K., Athimoolam, R., & Ayyavoo, J. (2015). Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using leaf extracts of Clitoria ternatea and Solanum nigrum and study of its antibacterial effect against common nosocomial pathogens. Journal of Nanoscience, 2015, 8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/928204 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/928204
Phanjom, P., Sultana, A., Sarma, H., Ramchiary, J., Goswami, K. & Baishya, P. (2012). Plant-mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Elaeagnus latifolia leaf extract. Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructure, 7(3), 1117-1123. https://chalcogen.ro/1117_Phanjom.pdf
Phanse, N., Venkataraman, K., Mishra, V., Shah, S. & Parikh, S. (2022). Biomediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles from Coriandrum sativum leaf extract: A green approach. International Journal for Modern Trends in Science and Technology, 8(05), 477-480. https://doi.org 10.46501/IJMTST0805072
Pradhan, S. (2013). Comparative analysis of silver nanoparticles prepared from different plant extracts (Hibiscus rosa sinensis, Moringa oleifera, Acorus calamus, Cucurbita maxima, Azadirachta indica) through green synthesis method, Ph.D. Thesis. National Institute of Technology, Rourkela.
Prajwala, B., Gopenath, T. S., Prasad, N., Raviraja, S., & Basalingappa, K. M. (2021). Green synthesis of silver nanoparticle by using Tinospora cordifolia leaf extract and its antimicrobial property. International Journal of Pharmaceutical Science & Research, 12(3), 1881-1886. http://dx.doi.org/10.13040/IJPSR.0975-8232.12(3).1881-86 DOI: https://doi.org/10.13040/IJPSR.0975-8232.12(3).1881-86
Prasad, S., & Srivastava, S. K. (2021). Oxidative stress and cancer: Antioxidative role of Ayurvedic plants. In Cancer, (Second Edition), 301-310. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-819547-5.00027-4 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-819547-5.00027-4
Rajathi, K., Vijaya Raj, D., Anarkal, J., & Sridhar, S. (2012). Green Synthesis, characterization and in-vitro antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles by using Tinospora cordifolia leaf extract. International Journal of Green Chemistry and Bioprocess, 2(2), 15-19.
Rajeshkumar, S., Santhiyaa, R. V., & Veena, P. (2018). Plant and its biomolecules on synthesis of silver nanoparticles for the antibacterial and antifungal activity in nanotechnology. In: The life sciences, edited by Prasad, R., Jha, A., DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-99570-0_6
Prasad, K. (eds) Exploring the realmns of nature for nanosynthesis nanotechnology in the life sciences. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-99570-0 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-99570-0
Rasheed, T., Bilal, M., Iqbal, H. M. N., & Li, C. (2017). Green biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using leaves extract of Artemisia vulgaris and their potential biomedical applications. Colloids Surf B: Biointerfaces, 158, 408-415. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2017.07.020 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2017.07.020
Selvam, K., Sudhakar, C., Govarthanan, M., Thiyagarajan, P., Sengottaiyan, A., Senthilkumar, B., & Selvankumar, T. (2017). Eco-friendly biosynthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles using Tinospora cordifolia (Thunb.) Miers and evaluate its antibacterial, antioxidant. Journal of Radiation Research and Applied Sciences, 10, 6-12. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jrras.2016.02.005 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrras.2016.02.005
Singh, K., Panghal, M., Kadyan, S., Chaudhary, U., & Yadav, J. P. (2014). Antibacterial activity of synthesized silver nanoparticles from Tinospora cordifolia against multi drug resistant strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from burn patients. Journal of Nanomedicine and Nanotechnology, 5(2), 1-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.4172/2157-7439.1000192 DOI: https://doi.org/10.4172/2157-7439.1000192
Zhang, Y., Cui, L., Lu, Y., He, J., Hussain, H., Xie, L., Sun, X., Meng, Z., Cao, G., Qin, D., & Wang, D. (2022). Characterization of silver nanoparticles synthesized by leaves of Lonicera japonica Thunb. International Journal of Nanomedicine, 17, 1647-1657. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S356919 DOI: https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S356919
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Nandini V. Phanse, Venkataraman Krishnaiah, Pravin A. Kekre, Sanjay Shah, Shilpa Parikh

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
1) Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
2) Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.
3) Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work.


