Effect of whole plant extract of Evolvulus alsinoides on thermal stress resistance and longevity in Caenorhabditis elegans
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14295/bjs.v4i2.695Keywords:
genus Caenorhabditis, genus Evolvulus, longevity studies, thermal resistanceAbstract
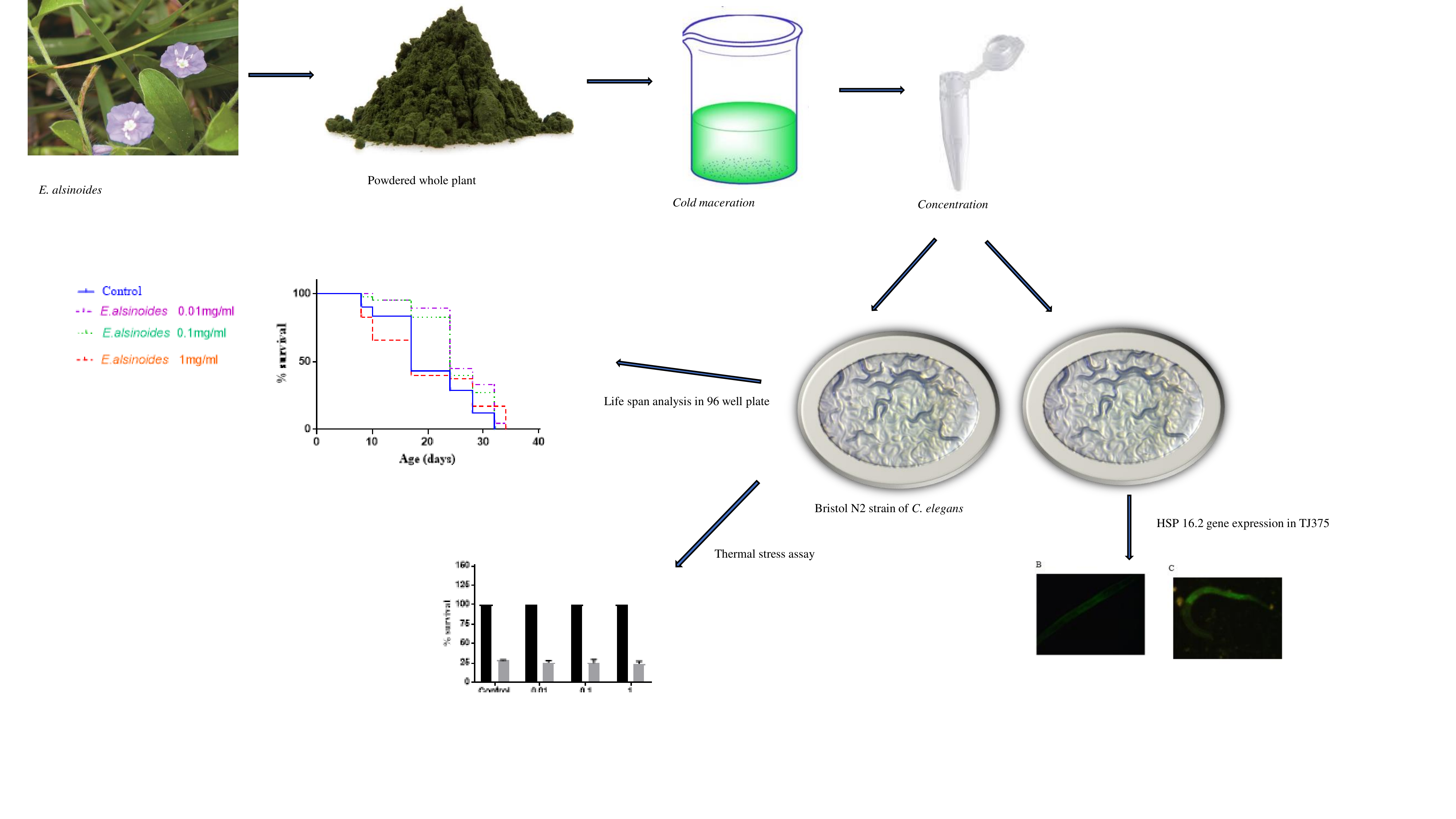
The popular Ayurvedic plant Evolvulus alsinoides is known to have adaptogenic properties. Adaptogens reduce stress and anxiety and thereby promote the overall well-being of the individual. Since chronic stress is associated with lower than normal lifespan expectance, any herbs known to reduce the stress should have the reverse impact. Therefore, this research aimed to study the anti-ageing activity of Evolvulus alsinoides in the well-established aging model Caenorhabditis elegans. The longevity-enhancing impact was assessed under the optimum growth and survival conditions for the C. elegans. Oxidative stress was induced by the use of Paraquat in N2 wild-type C. elegans, and the thermal stress was induced in transgenic C. elegans TJ 356, which expressed Green fluorescence Protein (GFP) under the control of heat shock protein promoters for the visualization of induction of anti-stress genes. The impact of the stress was analyzed by the lifespan analysis, and data were analyzed by the Kaplein Meyer statistical analysis. The results indicated that E. alsinoides extracts dose-dependently increased the mean lifespan of C. elegans by 18.0% and 26.2% at the concentrations of 0.1 mg/mL-1 and 1 mg/mL-1 under optimum growth and survival conditions, respectively. The survival rates of E. alsinoides extract-fed C. elegans have been greater than those of untreated C. elegans against thermal-induced stress. For Oxidative stress, the E. alsinoides treatment was non-significant. It was found that Evolvulus alsinoides extract promotes longevity in Caenorhabditis elegans by promoting stress tolerance and by tinkering with the insulin/IGF signaling pathway.
References
Asthana, J., Yadav, A. K., Pant, A., Pandey, S., Gupta, M. M., & Pandey, R. (2015). Specioside ameliorates oxidative stress and promotes longevity in Caenorhabditis elegans. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part C: Toxicology & Pharmacology, 169, 25-34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2015.01.002 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2015.01.002
Chen, A. L., Lum, K. M., Lara-Gonzalez, P., Ogasawara, D., Cognetta, A. B., To, A., Parsons, W. H., Simon, G. M., Desai, A., Petrascheck, M., Bar-Peled, L., & Cravatt, B. F. (2019). Pharmacological convergence reveals a lipid pathway that regulates C. elegans lifespan. Nature Chemical Biology, 15(5), 453-462. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41589-019-0243-4 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41589-019-0243-4
Dhanjal, D. S., Bhardwaj, S., Sharma, R., Bhardwaj, K., Kumar, D., Chopra, C., Nepovimova, E., Singh, R., & Kuca, K. (2020). Plant fortification of the diet for anti-ageing effects: A review. Nutrients, 12(10). https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12103008 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12103008
Doshi, S., & Braganza, V. (2018). Ameliorative effect of Argyreia boseana Sant. & Pat. On stress in Caenorhabditis elegans. Journal of Ayurveda and Integrative Medicine. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaim.2017.11.001 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaim.2017.11.001
Doshi, S., & Braganza, V. (2019). Longevity promoting effect of Catharanthus roseus (L.) G. Don in C.elegans is
modulated by daf-16 and other genes. In Biotechnology and Biological Sciences. CRC Press.
Duangjan, C., Rangsinth, P., Gu, X., Wink, M., & Tencomnao, T. (2019). Lifespan Extending and Oxidative Stress Resistance Properties of a Leaf Extracts from Anacardium occidentale L. in Caenorhabditis elegans. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/9012396 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/9012396
Esmaealzadeh, N., Iranpanah, A., Sarris, J., & Rahimi, R. (2022). A literature review of the studies concerning selected plant-derived adaptogens and their general function in body with a focus on animal studies. Phytomedicine, 105, 154354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154354 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154354
Gruber, J., Chen, C.-B., Fong, S., Ng, L. F., Teo, E., & Halliwell, B. (2015). Caenorhabditis elegans: What we can and cannot learn from aging worms. Antioxidants & Redox Signaling, 23(3), 256-279. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2014.6210 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2014.6210
Herald, T. J., Gadgil, P., & Tilley, M. (2012). High-throughput micro plate assays for screening flavonoid content and DPPH-scavenging activity in sorghum bran and flour. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 92(11), 2326–2331. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.5633 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.5633
Jayarathne, S., Ramalingam, L., Edwards, H., Vanapalli, S. A., & Moustaid-Moussa, N. (2020). Tart cherry increases lifespan in Caenorhabditis elegans by altering metabolic signaling pathways. Nutrients, 12(5). https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12051482 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12051482
Kumar, R., Gupta, K., Saharia, K., Pradhan, D., & Subramaniam, J. R. (2013). Withania somnifera root extract extends lifespan of Caenorhabditis elegans. Annals of Neurosciences, 20(1). https://doi.org/10.5214/ans.0972.7531.200106 DOI: https://doi.org/10.5214/ans.0972.7531.200106
Liao, V. H.-C. (2018). Use of Caenorhabditis elegans to study the potential bioactivity of natural compounds. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 66(8), 1737-1742. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.7b05700 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.7b05700
Min, H., Youn, E., Kawasaki, I., & Shim, Y.-H. (2017). Caffeine-induced food-avoidance behavior is mediated by neuroendocrine signals in Caenorhabditis elegans. BMB Reports, 50(1), 31-36. https://doi.org/10.5483/bmbrep.2017.50.1.126 DOI: https://doi.org/10.5483/BMBRep.2017.50.1.126
Muñoz, M. J. (2003). Longevity and heat stress regulation in Caenorhabditis elegans. Mechanisms of Ageing and Development, 124(1), 43-48. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0047-6374(02)00168-9 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0047-6374(02)00168-9
Park, H.-E. H., Jung, Y., & Lee, S.-J. V. (2017). Survival assays using Caenorhabditis elegans. Molecules and Cells, 40(2), 90-99. https://doi.org/10.14348/molcells.2017.0017 DOI: https://doi.org/10.14348/molcells.2017.0017
Pietsch, K., Saul, N., Menzel, R., Stürzenbaum, S. R., & Steinberg, C. E. W. (2009). Quercetin mediated lifespan extension in Caenorhabditis elegans is modulated by age-1, daf-2, sek-1 and unc-43. Biogerontology, 10(5), 565-578. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10522-008-9199-6 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10522-008-9199-6
Porta-de-la-Riva, M., Fontrodona, L., Villanueva, A., & Cerón, J. (2012). Basic Caenorhabditis elegans methods: Synchronization and observation. JoVE - Journal of Visualized Experiments, 64, e4019-e4019. https://doi.org/10.3791/4019 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3791/4019
Possik, E., & Pause, A. (2015). Measuring oxidative stress resistance of Caenorhabditis elegans in 96-well microtiter plates. Journal of Visualized Experiments: JoVE, 99, e52746. https://doi.org/10.3791/52746 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3791/52746
Poupet, C., Saraoui, T., Veisseire, P., Bonnet, M., Dausset, C., Gachinat, M., Camarès, O., Chassard, C., Nivoliez, A., & Bornes, S. (2019). Lactobacillus rhamnosus Lcr35 as an effective treatment for preventing Candida albicans infection in the invertebrate model Caenorhabditis elegans: First mechanistic insights. PloS One, 14(11), e0216184. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0216184 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0216184
Sadowska-Bartosz, I., & Bartosz, G. (2014). Effect of antioxidants supplementation on aging and longevity [Review Article]. BioMed Research International. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/404680 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/404680
Salehi, B., Azzini, E., Zucca, P., Maria Varoni, E., V. Anil Kumar, N., Dini, L., Panzarini, E., Rajkovic, J., Valere Tsouh Fokou, P., Peluso, I., Prakash Mishra, A., Nigam, M., El Rayess, Y., El Beyrouthy, M., N. Setzer, W., Polito, L., Iriti, M., Sureda, A., Magdalena Quetglas-Llabrés, M., & Sharifi-Rad, J. (2020). Plant-derived bioactives and oxidative stress-related disorders: A key trend towards healthy aging and longevity promotion. Applied Sciences, 10(3). https://doi.org/10.3390/app10030947 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/app10030947
Sen, R., Mukherjee, S., Paul, R., & Narula, R. (2019). Biotechnology and biological sciences: Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference of Biotechnology and Biological Sciences (BIOSPECTRUM 2019), August 8-10, 2019, Kolkata, India. CRC Press. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1201/9781003001614
Shen, N., Zeng, W., Leng, F., Lu, J., Lu, Z., Cui, J., Wang, L., & Jin, B. (2021). Ginkgo seed extract promotes longevity and stress resistance of Caenorhabditis elegans. Food & Function, 12(24), 12395-12406. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1fo02823e DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/D1FO02823E
Siripurapu, K. B., Gupta, P., Bhatia, G., Maurya, R., Nath, C., & Palit, G. (2005). Adaptogenic and anti-amnesic properties of Evolvulus alsinoides in rodents. Pharmacology, Biochemistry, and Behavior, 81(3), 424-432. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbb.2005.03.003 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbb.2005.03.003
Slimen, I. B., Najar, T., Ghram, A., Dabbebi, H., Mrad, M. B., & Abdrabbah, M. (2014). Reactive oxygen species, heat stress and oxidative-induced mitochondrial damage. A review. International Journal of Hyperthermia, 30(7), 513-523. https://doi.org/10.3109/02656736.2014.971446 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3109/02656736.2014.971446
Solis, G. M., & Petrascheck, M. (2011). Measuring Caenorhabditis elegans life span in 96 well microtiter plates. Journal of Visualized Experiments: JoVE, 49. https://doi.org/10.3791/2496 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3791/2496-v
Tissenbaum, H. A. (2015). Using C. elegans for aging research. Invertebrate Reproduction & Development, 59(sup1), 59–63. https://doi.org/10.1080/07924259.2014.940470 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/07924259.2014.940470
Tollefsbol, B. L. Q., & T. O. (2010, January 31). Polyphenols and Aging. Current Aging Science. http://www.eurekaselect.com/95385/article
Van Raamsdonk, J. M., & Hekimi, S. (2010). Reactive oxygen species and aging in Caenorhabditis elegans: Causal or casual relationship? Antioxidants & Redox Signaling, 13(12), 1911-1953. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2010.3215 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2010.3215
Wiegant, F. a. C., Surinova, S., Ytsma, E., Langelaar-Makkinje, M., Wikman, G., & Post, J. A. (2009). Plant adaptogens increase lifespan and stress resistance in C. elegans. Biogerontology, 10(1), 27-42. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10522-008-9151-9 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10522-008-9151-9
Yadav, M. K., Singh, S. K., Singh, M., Mishra, S. S., Singh, A. K., Tripathi, J. S., & Tripathi, Y. B. (2019). Neuroprotective activity of Evolvulus alsinoides & Centella asiatica ethanolic extracts in scopolamine-induced amnesia in swiss albino mice. Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences, 7(7), 1059-1066. https://doi.org/10.3889/oamjms.2019.247 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3889/oamjms.2019.247
Zhang, J., Xiao, Y., Guan, Y., Rui, X., Zhang, Y., Dong, M., & Ma, W. (2019). An aqueous polyphenol extract from Rosa rugosa tea has antiaging effects on Caenorhabditis elegans. Journal of Food Biochemistry, 43(4), e12796. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfbc.12796 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/jfbc.12796
Zhu, B., Jo, K., Yang, P., Tohti, J., Fei, J., & Abudukerim, K. (2019). Aiweixin, a traditional uyghur medicinal formula, extends the lifespan of Caenorhabditis elegans. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine, 2019(1), 3684601. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/3684601 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/3684601
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Shital Hemal Doshi

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
1) Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
2) Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.
3) Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work.


