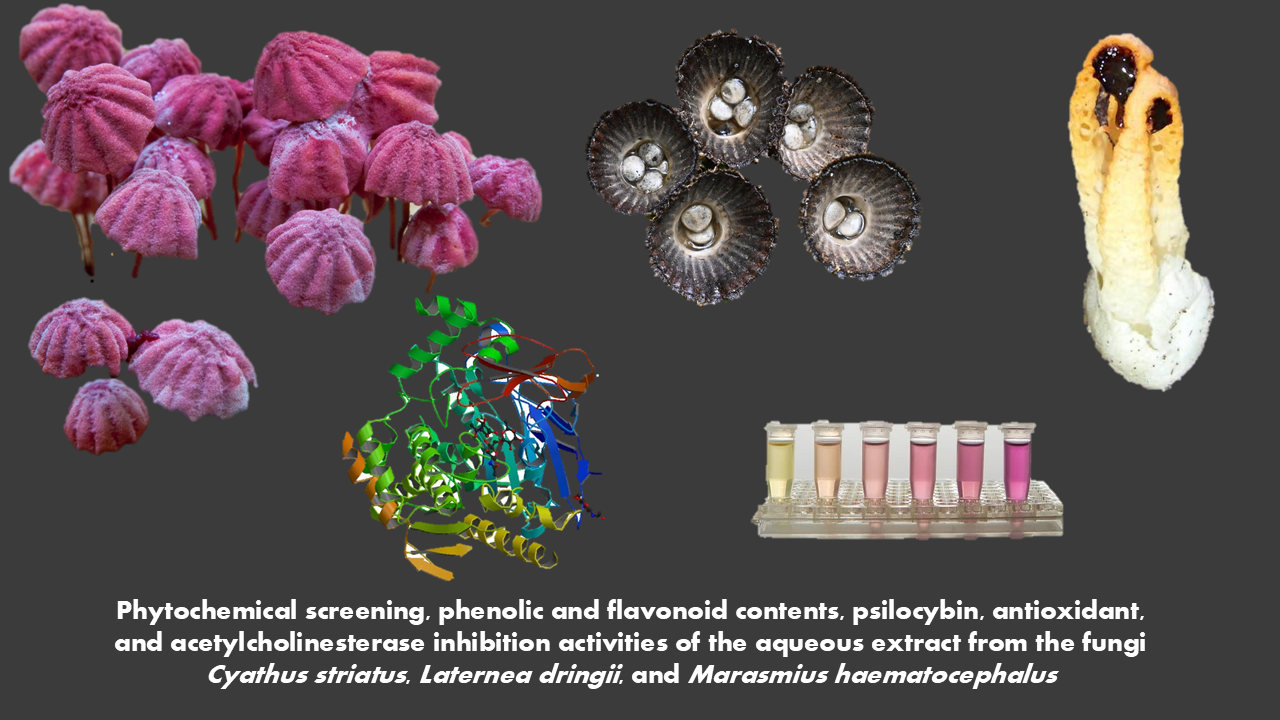
Phytochemical screening, phenolic and flavonoid contents, psilocybin, antioxidant, and acetylcholinesterase inhibition activities of the aqueous extract from the fungi Cyathus striatus, Laternea dringii, and Marasmius haematocephalus
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14295/bjs.v3i11.694Keywords:
Cyathus Genus, Laternea Genus, Marasmius Genus, Fungal extract, MushroomsAbstract
Various families of mushrooms contain important phytochemicals with significant potential. This study aimed to investigate the phytochemical prospecting, presence of psilocybin, antioxidant activities, and acetylcholinesterase inhibition in aqueous extracts of Cyathus striatus, Laternea dringii, and Marasmius haematocephalus. Aqueous extracts were produced from mushrooms, and phytochemical groups were determined. The total phenolic and flavonoid content, DPPH reduction capacity, and FRAP were quantitatively determined. The acetylcholinesterase inhibition assay was performed, and the results were expressed as AChE inhibition percentages. Phytochemical groups such as flavonoids, phenolics, alkaloids, organic acids, and aliphatic compounds were positively detected. For phenolics, the extracts showed values of 208.44, 134.11, and 100.09 mg GAE g TPC-1; for flavonoids, values of 45.12, 56.06, and 39.71 mg QE g TFC-1. The FRAP reduction capacity showed values of 7.56, 14.43, and 4.15 µM TE g-1, while for DPPH, the values were 100.07, 88.12, and 133.65 µg mL-1. Low, medium, and strong AChE inhibition activity was observed with values of 43.11%, 68.53%, and 77.14%, respectively, for C. striatus, L. dringii, and M. haematocephalus. The aqueous extracts of Cyathus striatus, Laternea dringii, and Marasmius haematocephalus exhibited various phytomolecules groups with potential biological activities observed in this study.
References
Afewerki, S., Wang, J. X., Liao, W. W., Córdova, A. (2019). The chemical synthesis and applications of tropane alkaloids. The alkaloids: Chemistry and Biology, 81, 151-233. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.alkal.2018.06.001 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.alkal.2018.06.001
Allbutt, A. D., Ayer, W. A., Brodie, H. J., Johri, B. N., Taube, H. (1971). Cyathin, a new antibiotic complex produced by Cyathus helenae. Can. J. Microbiol, 17, 1401-1407. https://doi.org/10.1139/m71-223 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1139/m71-223
Anke, T., Oberwinkler, F., Steglich, W., Höfle, G. (1977). The striatins – New antibiotics from the Basidiomycete Cyathus striatus (Huds. Ex Pers.) Willd. The Journal of Antibiotics, 30(3), 221-225. https://doi.org/10.7164/antibiotics.30.221 DOI: https://doi.org/10.7164/antibiotics.30.221
Antonín, V, Noordeloos, M. E. (2010). A Monograph of marasmioid and collybioid fungi in Europe. IHW-Verlag, Eching.
Asatiani, M. D., Elisashvili, V. I., Wasser, S. P., Reznick, A. Z., Nevo, R. (2007). Free-radical scavenging activity of submerged mycelium extracts from higher basidiomycetes mushrooms. Bioscience Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, 71, (12), 3090-3092. https://doi.org/10.1271/bbb.70280 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1271/bbb.70280
Awang, K., Loong, X. M., Leong, K. H., Supratman, U., Litaudon, M., Mukhtar, M. R. (2012). Triterpenes and steroids from the leaves of Aglaia exima (Meliaceae). Fitoterapia, 83(8), 1391-1395. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fitote.2012.10.004 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fitote.2012.10.004
Ayer, W. A., Reffstrup, T. (1982). Metabolites of bird’s nest fungi. Part 18. new oxygenated cadinane derivatives from Cyathus striatus. Tetrahedron, 38, 1409-1412. https://doi.org/10.1016/0040-4020(82)80221-4 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0040-4020(82)80221-4
Ayer, A.W., Flanagan, R.J., Reffstrup, T. (1984). Metabolites of bird’s nest fungi-19. Tetrahedron, 40, 2069-2082. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0040-4020(01)88448-9
Bai, R., Zhang, C-C., Yin, X., Wei, J., Gao, J-M. (2015). Striatoids A-F, cyathane diterpenoids with neurotrophic activity from cultures of the fungus Cyathus striatus. Journal of Natural Products, 78(4), 783-788. http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/np501030r DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/np501030r
Bhambri, A., Srivastava, M., Mahale, V. G., Mahale, S., Karn, S. K. (2022). Mushrooms as potential sources of active metabolites and medicines. Frontiers in Microbiology, 13, 837266. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2022.837266 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2022.837266
Balamurugan, V., Sheerin Fatima, M. A., Velurajan, S. A guide to phytochemical analysis. International Journal of Advance Research and Innovative Ideas in Education - IJARIIE, 5(1), 236-245, 2019. https://doi.org/10.0415/IJARIIE-9430
Carvalho, G. G., Peres, G. C., Mendonça, R. M. C., Santos Filho, E. X. (2020). Phytochemical prospection and antibacterial activity of native plants from the cerrado of goiás, Brazil. Journal of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry, 9(2), 29-37.
Chang, S. T., Wasser, S. P. (2018). Current and future research trends in agricultural and biomedical applications of medicinal mushrooms and mushroom products (Review). International Journal of Medicinal Mushrooms, 20(12), 1121-1133. https://doi.org/10.1615/IntJMedMushrooms.2018029378 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1615/IntJMedMushrooms.2018029378
Chaudhary, P., Panth, N., Raut, B. K., Shrestha, N. P. N., Shakya, S., Mishra, B. B. T. A. D., Parajuli, N. (2023). Biochemical, antimicrobial, and antioxidant activities of some wild mushrooms from Nepal. Bibechana, 20(2), 161-175. https://doi.org/10.3126/bibechana.v20i2.54887 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3126/bibechana.v20i2.54887
Chudzik, M., Korzonek-SzlachetA, I., Król, W. (2015). Triterpenes as potentially cytotoxic compounds. Molecules, 20, 1610-1625, 2015. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20011610 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20011610
Coelho, M. F. B., Maia, S. S. S., Oliveira, A. K., Diógenes, F. E. P. (2011). Atividade alelopática de extrato de sementes de juazeiro. Horticultura Brasileira, 29(1), 108-111. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0102-05362011000100018 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1590/S0102-05362011000100018
Cortez, V., Baseia, I. G., Silveira, R. M. B. (2011a). Two noteworthy phallus from southern Brazil. Mycoscience, 52(6), 436-438, 2011a. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10267-011-0124-5 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/S10267-011-0124-5
Cortez, V. G., Baseia, L. G., Sliveira, R. M. B. (2011b). Gasteroid mycobiota of Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil: Lysuraceae (Basidiomycota). Acta Scientiarum, Biological Science, 33(1), 87-92. https://doi.org/10.4025/actascibiolsci.v33i1.6726 DOI: https://doi.org/10.4025/actascibiolsci.v33i1.6726
Fattorusso, E., Giovannitti, B., Lanzotti, V., Magno, S., Violante, U. (1992). 4,4-Dimethyl-5 alpha-ergosta-8,24(28)-dien-3 beta-ol from the fungus Marasmius oreades. Steroids, 57, 119-121. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0039-128X(92)90069-L
Forzza, R.C. (2010). Catálogo de Plantas e Fungos do Brasil. Instituto de Pesquisa Jardim Botânico do Rio de Janeiro, Rio de Janeiro, 1.
Gross, S. T. (2000). Detecting psychoactive drugs in the Developmental stages of mushrooms. Journal of Forensic Science, 45(3), 527-537. https://doi.org/10.1520/JFS14725J DOI: https://doi.org/10.1520/JFS14725J
Han, J., Chen, Y., Bao, L., Yang, X., Liu, D., LI, S., Zhao, F., Liu, H. (2013). Anti-inflammatory and cytotoxic cyathane diterpenoids from the medicinal fungus Cyathus africanus. Fitoterapia, 84, 22-31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fitote.2012.10.001 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fitote.2012.10.001
Hibbett, D. S., Bauer, R., Binder, M., Giachini, A. J. (2014).14 Agaricomycetes. Systematics and Evolution: The Mycota, 7(2), 373-429. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-55318-9_14
Hosaka, K., Bates, S. T., Beever, E. R., Castellano, M. A. (2006). Molecular phylogenetics of the gomphoid-phalloid fungi with an establishment of the new subclass Phallomycetidae and two new orders. Mycologia, 98(6), 949-959. https://doi.org/10.3852/mycologia.98.6.949 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/15572536.2006.11832624
Jameel, E., Umar, T., Kumar, J., Hoda, N. (2016). Coumarin: A privileged scaffold for the design and development of antineurodegenerative agents. Chemical Biology & Drug Design, 87(1), 21-38, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1111/cbdd.12629 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/cbdd.12629
Jenkinson, T. S., Perry, B. A., Schaefer, R. E., Desjardin, D. E. (2014). Cryptomarasmius gen. nov. established in the Physalacriaceae to accommodate members of Marasmius sect. Hygrometrici. Mycologia, 106(1), 86-94. https://doi.org/10.3852/11-309 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3852/11-309
Johri, B. N., Brodie, H. J. (1971). Extracellular production of indolics by the fungus Cyathus. Mycologia, 63, 736-744. https://doi.org/10.1080/00275514.1971.12019165 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/00275514.1971.12019165
Li, Y., Jiang, J. G. (2018). Health functions and structure-activity relationships of natural anthraquinones from plants. Food & Function, 9(12), 6063-6080. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8fo01569d DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/C8FO01569D
Liermann, J. C., Thines, E., Opatz, T., Anke, H. (2012). Drimane sesquiterpenoids from Marasmius sp. inhibiting the conidial germination of plant-pathogenic fungi. Journal of Natural Products, 75, 1983-1986. https://doi.org/10.1021/np300337w DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/np300337w
Lima, A. A., Gurgel, R. A. F., Oliveira, R. L., Ferreira, R. J., Barbosa, M. M. B., Baseia, I. G. (2019). New records of Phallales (Basidiomycota) from Brazilian semi-arid region. Current Research in Environmental & Applied Mycology, 9(1), 15-24. https://doi.org/10.5943/cream/9/1/2 DOI: https://doi.org/10.5943/cream/9/1/2
Machado, T. H. L., Menezes Filho, A. C. P., Ventura, M. V. A., Taques, A. S., Romão, T. C. (2024). First report of Laternea dringii, Phallales (Agaricomycetes) in the Central-West, State of Goiás, Brazil. Brazilian Journal of Science, 3(2), 173-178. https://doi.org/10.14295/bjs.v3i2.536 DOI: https://doi.org/10.14295/bjs.v3i2.536
Magnago, A. C., Trierveiler-Pereira, L., Neves, M. A. (2013). Phallales (Agaricomycetes, Fungi) from the tropical Atlantic Forest of Brazil. Journal of the Torrey Botanical Society, 140(2), 236-244. https://doi.org/10.3159/TORREY-D-12-00054.1 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3159/TORREY-D-12-00054.1
Maguire, J. D. (1962). Speed of germination-aid in selection evaluation for seedling emergence and vigor. Crop Science, 2, 176-177. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci1962.0011183X000200020033x DOI: https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci1962.0011183X000200020033x
Malik, E. M., Mülle, C. E. (2016). Anthraquinones as pharmacological tools and drugs. Medicinal Research Reviews, 36(4), 705-748. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/med.21391
Moncalvo, J.-M., Vilgalys, R., Redhead, S. A., Johnson, J. E., James, T. Y., Aime, M. C., Hofstetter, V., Verduin, S. J. W., Larsson, E., Baroni, T. J., Thorn, R. G., Jacobsson, S., Clémençon, H., Miller, Jr. O. K. (2002). One hundred and seventeen clades of euagarics. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 23(3), 357-400. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1055-7903(02)00027-1 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1055-7903(02)00027-1
Novanna, M., Ethiraj, K. R., Kannadasan, S. (2019). An overview of synthesis of indole alkaloids and biological activities of secondary metabolites isolated from Hyrtios species. Mini-Reviews in Medicinal Chemistry, 19(3), 194-205. https://doi.org/10.2174/1389557518666181102110537 DOI: https://doi.org/10.2174/1389557518666181102110537
Oliveira, J. J. S., Capelari, M., Margaritescu, S., Moncalvo, J.-M. (2002). Disentangling cryptic species in the Marasmius haematocephalus (Mont.) Fr. and M. siccus (Schwein.) Fr. species complexes (Agaricales, Basidiomycota). Cryptogamie. Mycologie, 43(5), 91-137. https://doi.org/10.5252/cryptogamie-mycologie2022v43a5 DOI: https://doi.org/10.5252/cryptogamie-mycologie2022v43a5
Oliveira, V. R. T., Barbosa, D. Í., Cavalcanti, L. H. (2024). Distribution of Badhamiopsis and Badhamia (Physaraceae, Mycomycetes) in brazilian biomes. Anais da Academia Brasileira de Ciências, 96(1), e20220698. https://doi.org/10.1590/0001-3765202420220698 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1590/0001-3765202420220698
Prusty, J. S., Kumar, A. (2019). Coumarins: antifungal effectiveness and future therapeutic scope. Molecular Diversity. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11030-019-09992-x DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11030-019-09992-x
Qi, J., Gao, Y-Q., Kang, S-J., Liu, C., Gao, J-M. (2023). Secondary metabolites of bird’s nest fungi: Chemical structures and biological activities. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 71(17), 6513-6524. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.4c06809 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.3c00904
Rocha, W. S., Lopes, R. M., Silva, D. B., Vieira, R. F., Silva, J. P., Agostini-Costa, T. S. (2011). Compostos fenólicos totais e taninos condensados em frutas nativas do cerrado. Revista Brasileira de Fruticultura, 33(4), 1215-1221. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-29452011000400021 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-29452011000400021
Schmitz, W., Saito, A. Y., Estevão, D., Saridakis, H. O. (2005). O chá verde e suas ações como quimioprotetor. Semina: Ciências Biológicas e da Saúde, 26(2), 119-130. https://doi.org/10.5433/1679-0367.2005v26n2p119 DOI: https://doi.org/10.5433/1679-0367.2005v26n2p119
Sharvit, L., Bar-Shalom, R., Azzam, N., Yechiel, Y., Wasser, S., Fares, F. (2021). Cyathus striatus extract induces apoptosis in human pancreatic cancer cells and inhibits xenograft tumor growth in vivo. Cancers, 13(9), 2017. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13092017 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13092017
Silva, N. A., Vieira, B. S., Ribeiro, G. M., Felisbino, J. K. R. P., Sousa, R. M. F. (2020). Atividade fitotóxica de um filtrado de cultura de Cercospora brachiata sobre sementes e parte aérea de Amaranthus viridis. Agrarian, 13(49), 339-351. https://doi.org/10.30612/agrarian.v13i49.9660 DOI: https://doi.org/10.30612/agrarian.v13i49.9660
Sommano, S. R., Suksathan, R., Sombat, T., Seehanam, P., Sirilun, S., Ruksiriwanich, W., Wangtueai, S., Leksawasdi, N. (2022). Nome perspective of medicinal mushroom cultivation: A review case for ‘magic’ mushrooms. Agronomy, 12(12), 3185. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12123185 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12123185
Souza, R. K. D., Mendonça, A. C. A. M., Silva, M. A. P. (2013). Aspectos etnobotânicos, fitoquímicos e farmacológicos de espécies de Rubiaceae no Brasil. Revista Cubana de Plantas Medicinais, 18(1), 140-156.
Stefanachi, A., Leonetti, F., Pisani, L., Catto, M., Carotti, A. (2018). Coumarin: A natural, privileged and versatile scaffold for bioactive compounds. Molecules, 23(2), 250. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23020250 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23020250
Teixeira-Silva, M. A., Silva, C. G., Santos, G. S., Carvalho, C. M., Cortez, V. G., Silveira, M. (2024). Macrofungal species richness and composition of Acre state, Amazon, Brazil: State of the art. The Botanical Review, 90, 186-220. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12229-024-09302-7 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12229-024-09302-7
Toledo, A. G., Souza, J. G. L., Santana, C. B., Mallmann, A. P., Santos, C. V., Corrêa, J. M., Pinto, F. G. S. (2021). Antimicrobial, antioxidant activity and phytochemical prospection of Eugenia involucrata DC. leaf extracts. Brazilian Journal of Biology, 83, e245753. https://doi.org/10.1590/1519-6984.245753 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1590/1519-6984.245753
Ur Rashid, M., Alamzeb, M., Ali, S., Ullah, Z., Shah, Z. A., Naz, I. (2019). The chemistry and pharmacology of alkaloids and allied nitrogen compounds from Artemisia species: A review. Phytotherapy Research, 33(10), 2661-2684. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.6466 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.6466
Xu, M., Kang, X., LI, Q., Liang, Y., Zhang, M., Gong, Y., Chen, C., Zhu, H., Zhang, Y. (2022). Thirteen cyathane diterpenoids with acetylcholinesterase inhibitory effects from the fungus Cyathus africanus. Phytochemistry, 193, 112982. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2021.112982 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2021.112982
Zhang, J., Wang, P., Fang, L., Zhang, Q-A., Yan, C., Chen, J. (2017). Isolation and characterization of phosphate-solubilizing bacteria from mushroom residues and their effect on tomato plant growth promotion. Polish Journal of Microbiology, 66(1), 57-65. https://doi.org/10.5604/17331331.1234993 DOI: https://doi.org/10.5604/17331331.1234994
Yang, N. N., Ma, Q. Y., Yang, L., Xie, Q. Y., Kong, F. D., Dai, H. F., Yu, Z. F., Zhao, Y. X. (2021). Two new compounds from mycelial fermentation products with nematicidal activity of Marasmius berteroi. Phytochemistry Letters, 44, 106-109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytol.2021.06.004 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytol.2021.06.004
Yang, N. N., Ma, Q. Y., Kong, F. D., Xie, Q. Y., Dai, H. F., Zhou, L. M., Yu, Z. F., Zhao, Y. X. (2020). Napthrene compounds from mycelial fermentation products of Marasmius berteroi. Molecules, 25(17), 3898-3906. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25173898 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25173898
Zhang, L., Yang, M., Song, Y., Sun, Z., Peng, Y., Qu, K., Zhu, H. (2009). Antihypertensive effect of 3,3,5,5-tetramethyl-4-piperidone, a new compound extracted from Marasmius androsaceus. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 123, 34-39. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2009.02.033
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Douglas Ferreira da Silva, Antonio Carlos Pereira de Menezes Filho, Aurélio Ferreira Melo, Porshia Sharma, Tullyo Henrique Lima Machado, Vanêcia Oliveira Cunha Machado, Matheus Vinícius Abadia Ventura

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
1) Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
2) Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.
3) Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work.


