Exploring the photo-catalytic degradation of methyl orange dye using Strontium doped Bismuth oxide nanoparticles
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14295/bjs.v3i1.488Keywords:
photocatalysis, dye degradation, Bismuth oxide, doping, characterization, methyl orangeAbstract
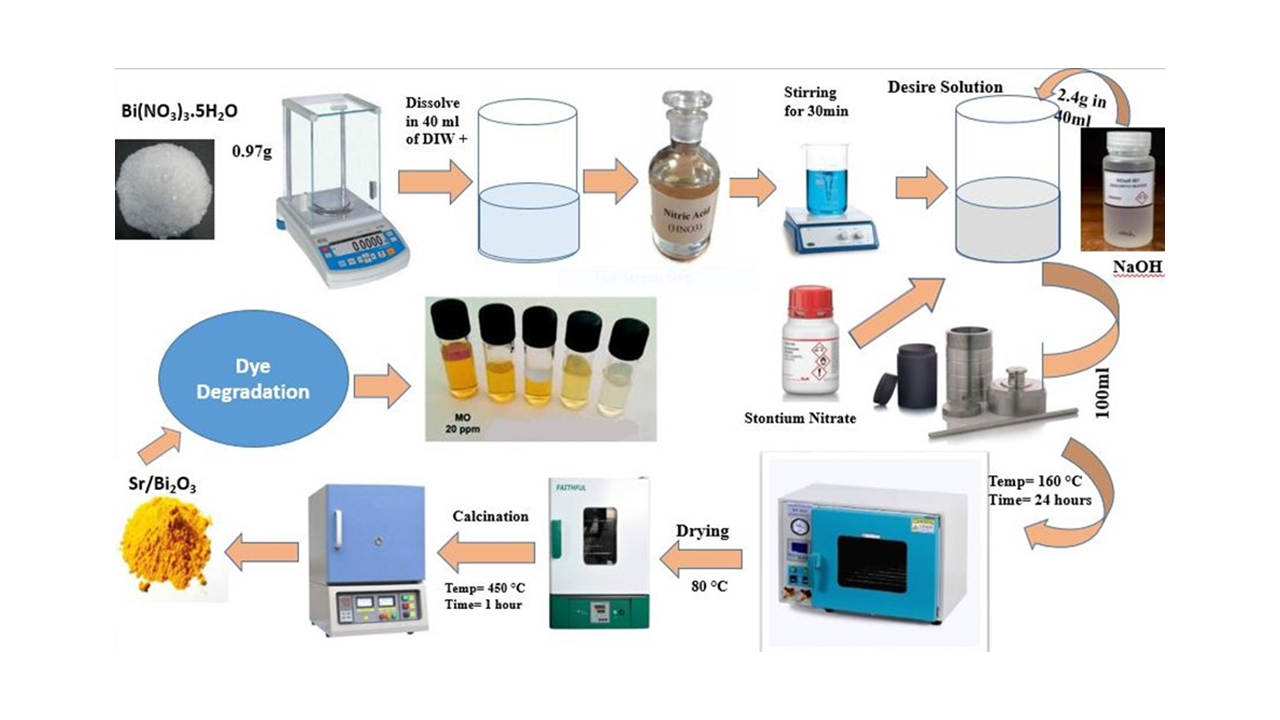
Low dimensional metal oxide Nps have garnered significant attention due to their distinctive characteristics and diverse application domains. This investigation can provide further elucidation regarding the synthesis of Strontium doped-Bi2O3 efficacious photocatalysts operating under visible light, thereby potentially addressing environmental quandaries. The photoactivity of Strontium doped-Bi2O3 Nps exhibits a significantly greater magnitude when compared to that of Bi2O3 nanoparticles lacking Strontium doping. The hydrothermal method shall be employed for the synthesis of Strontium-doped Bismuth oxide in the course of preparation. A solution of NH4OH will be introduced to Bismuth nitrate and Strontium chloride. The resulting mixtures shall be subjected to vigorous stirring for a duration of 1 hour, after which they will be transferred into 100 mL autoclaves made of stainless steel and equipped with Teflon liners. These autoclaves shall then be heated to a temperature of 180 °C for a period of 6 h. The prepared samples shall subsequently undergo collection and undergo multiple washes utilising de-ionized water. In order to synthesise Strontium doped-Bi2O3 is imperative to subject the resulting compound to a subsequent calcination process at a temperature of 450° C. Infra-Red spectroscopy (FT-IR), UV-Visible, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), techniques shall be employed for the investigation of the crystalline structures and morphologies of the powder. The resultant specimen shall subsequently serve as a catalyst for the photolytic degradation of organic dye methyl orange under diverse illumination circumstances. UV-Visible spectroscopy shall subsequently be employed to monitor the extent of photocatalytic efficacy.
References
Ai, Z., Huang, Y., Lee, S., & Zhang, L. (2011). Monoclinic α-Bi2O3 photocatalyst for efficient removal of gaseous NO and HCHO under visible light irradiation. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 509(5), 2044-2049. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2010.10.132 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2010.10.132
Ali, A. (2023). Synthesis of Silver oxide nanoparticles and its antimicrobial, anticancer, anti-inflammatory, wound healing, and immunomodulatory activities-A review. Acta Scientific Applied Physics, 3(7), 33-48.
Baia, L., Stefan, R., Kiefer, W., Popp, J., & Simon, S. (2002). Structural investigations of copper doped B2O3–Bi2O3 glasses with high bismuth oxide content. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 303(3), 379-386. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-3093(02)01042-6 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-3093(02)01042-6
Boulkroune, R., Sebais, M., Messai, Y., Bourzami, R., Schmutz, M., Blanck, C., Halimi, O., & Boudine, B. (2019). Hydrothermal synthesis of strontium-doped ZnS nanoparticles: structural, electronic and photocatalytic investigations. Bulletin of Materials Science, 42, 1-8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-019-1905-2 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-019-1905-2
Ghani, I., Kashif, M., Khattak, O. A., Shah, M., Nawaz, S., Ullah, S., Murad, S., Naz, S., Khan, H. W., & Muhammad, S. (2023). Hydrothermal synthesis and characterization of Cobalt doped Bismuth oxide NPs for photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange dye. Journal of Xi’an Shiyou University, 19(7), 1195-1217. https://www.xisdxjxsu.asia/V19I07-76.pdf
Ghule, B. G., Shinde, N. M., Nakate, Y. T., Jang, J.-H., & Mane, R. S. (2022). Bismuth oxide-doped graphene-oxide nanocomposite electrode for energy storage application. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 651, 129690. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2022.129690 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2022.129690
Hamza, M., Muhammad, S., & Zahoor, S. (2022). Biologically synthesized Zinc oxide nanoparticles and its effect – A review. Acta Scientific Applied Physics, 2(9), 03-10.
Horikoshi, S., & Serpone, N. (2013). Introduction to nanoparticles. Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Published, 1-24. https://application.wiley-vch.de/books/sample/3527331972_c01.pdf DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/9783527648122.ch1
Kashif, M., Muhammad, S., Ali, A., Ali, K., Khan, S., Zahoor, S., & Hamza, M. (2023). Bismuth oxide nanoparticle fabrication and characterization for photocatalytic bromophenol blue degradation. Journal of Xi’an Shiyou University, 19(7), 521-544.
Kim, J., Kimura, T., & Yamaguchi, T. (1989). Sintering of Zinc oxide doped with Antimony oxide and Bismuth oxide. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 72(8), 1390-1395. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1151-2916.1989.tb07659.x DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1151-2916.1989.tb07659.x
Liu, X., Cao, H., & Yin, J. (2011). Generation and photocatalytic activities of Bi@Bi2O3 microspheres. Nano Research, 4, 470-482. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-011-0103-3 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-011-0103-3
Lu, H., Wang, S., Zhao, L., Dong, B., Xu, Z., & Li, J. (2012). Surfactant-assisted hydrothermal synthesis of Bi2O3 nano/microstructures with tunable size. Royal Society of Chemistry, 2, 3374-3378. https://doi.org/10.1039/C2RA01203K DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/c2ra01203k
Muhammad, S., Ali, A., Shah, J., Hamza, M., Kashif, M., Khel, B. K. A., & Iqbal, A. J. N. (2023). Using Moringa oleifera stem extract for green synthesis, characterization, and anti-inflammatory activity of Silver oxide nanoparticles. Natural and Applied Sciences International Journal, 4(1), 80-97. https://doi.org/10.47264/idea.nasij/4.1.6 DOI: https://doi.org/10.47264/idea.nasij/4.1.6
Qiu, Y., Yang, M., Fan, H., Zuo, Y., Shao, Y., Xu, Y., Yang, X., & Yang, S. (2011). Nanowires of α- and β-Bi2O3: phase-selective synthesis and application in photocatalysis. From the Journal: CrystEngComn, 6 1843-1850. https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2011/ce/c0ce00508h/unauth DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/C0CE00508H
Zaman, S., Kashif, M., Shah, M., Hameed, A., Majeed, N., Ismail, M., Khan, I., Ullah, S., & Khan, N. (2024). Investigating the enhanced photocatalytic degradation of bromophenol blue using Ni/Zn co-doped Strontium oxide nanoparticles synthesized via hydrothermal method. Brazilian Journal of Science, 3(1), 102-114. https://doi.org/10.14295/bjs.v3i1.460 DOI: https://doi.org/10.14295/bjs.v3i1.460
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Taimoor Ahmad, Osama Ali Khattak, Shah Nawaz, Saif Ullah, Jalal Amir, Muhammad Atif, Bahar Ali, Mansoor Jamal, Ihsan Ghani, Shafaq Murad, Abdur Raziq

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
1) Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
2) Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.
3) Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work.


