Investigating the enhanced photocatalytic degradation of bromophenol blue using Ni/Zn co-doped Strontium Oxide nanoparticles synthesized via hydrothermal method
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14295/bjs.v3i1.460Keywords:
Ni and Zn co-doped Strontium oxide, hydrothermal method, nanoparticles, photocatalytic degradation and bromophenol blueAbstract
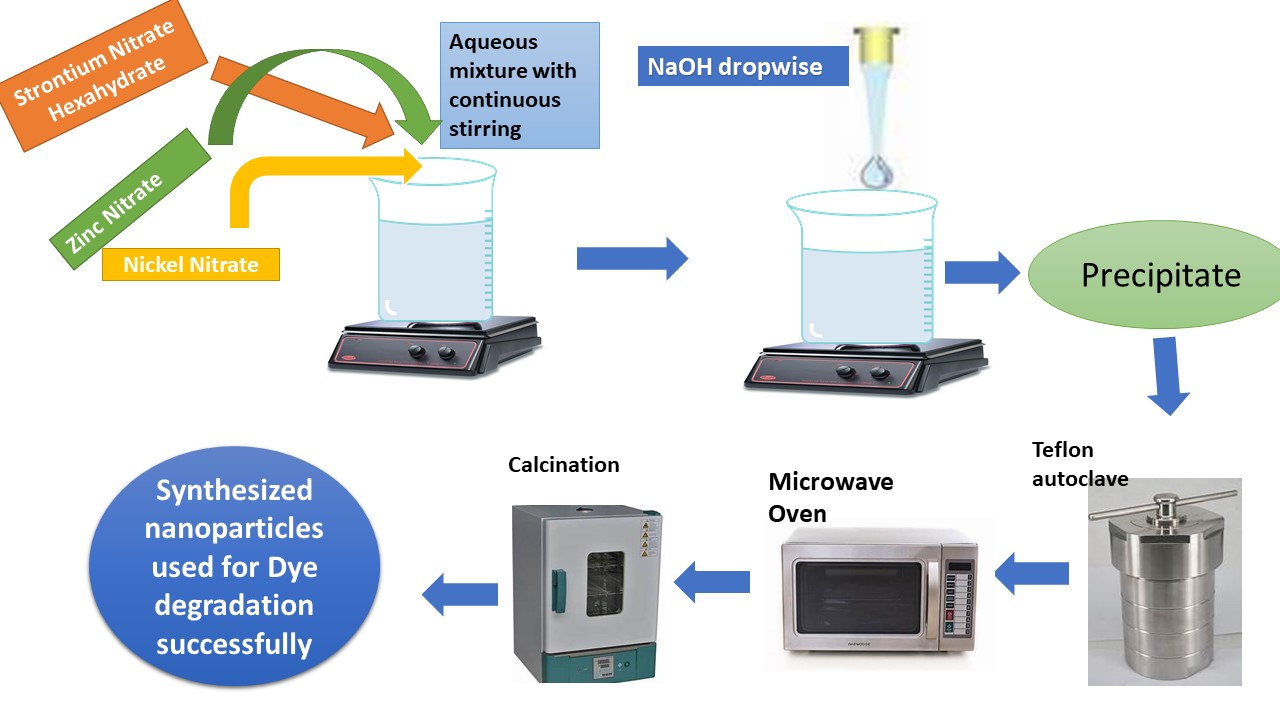
Excessive exposure of human to organic contaminants from industrial effluents calls for the implementation of effective pollutants removal techniques. This article investigates the photocatalytic degradation of bromophenol blue dye using Strontium oxide nanoparticles co-doped with Nickel and Zinc. Hydrothermal synthesis produced the nanoparticles, which were subsequently characterized using various analytical techniques. UV/Visible revealed absorption peaks at 294 nm, 306 nm, 311 nm, and 318 nm, while FTIR spectroscopy identified stretching peaks at 416 cm-1, 588 cm-1, and 856 cm-1 for Ni-O and Sr-O bonds. The nanoparticles displayed diameters ranging from 30.50 nm to 36.97 nm. EDX analysis confirmed the elemental composition, with Sr and O comprising of approximately 82.02 %, and Ni and Zn approximately 3.21%. Photocatalytic degradation experiments demonstrated that SrO nanoparticles 85.42% degradation efficiency, while co-doped SrO nanoparticles achieved an impressive 97.97% degradation efficiency. This work highlights the potential co-doped SrO nanoparticles as a promising solution for the efficient removal of organic pollutants from the industrial wastewater, addressing environment contamination concerns.
References
Ahmad, I., Aslam, M., Jabeen, U., Zafar, M. N., Malghani, M. N. K., Alwadai, N., Alshammari, F. H., Almuslem, A. S., & Ullah, Z. (2022). ZnO and Ni-doped ZnO photocatalysts: Synthesis, characterization and improved visible light driven photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue. Inorganica Chimica Acta, 543, 121167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ica.2022.121167 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ica.2022.121167
Akpomie, K. G., Adegoke, K. A., Oyedotun, K. O., Ighalo, J. O., Amaku, J. F., Olisah, C., Adeola, A. O., Iwuozor, K. O., & Conradie, J. (2022). Removal of bromophenol blue dye from water onto biomass, activated carbon, biochar, polymer, nanoparticle, and composite adsorbents. Biomass Conversion and Biorefinery, 1-29. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-022-03592-w DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-022-03592-w
Alam, M. W., Aamir, M., Farhan, M., Albuhulayqah, M., Ahmad, M. M., Ravikumar, C. R., Kumar, V. G., & Murthy, H. C. A. (2021). Green synthesis of Ni-Cu-Zn based nanosized metal oxides for photocatalytic and sensor applications. Crystals, 11(12), 1467. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11121467 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11121467
Al-Mamun, M. R., Hossain, K. T., Mondal, S., Khatun, M. A., Islam, M. S., & Khan, M. Z. H. (2022). Synthesis, characterization, and photocatalytic performance of methyl orange in aqueous TiO2 suspension under UV and solar light irradiation. South African Journal of Chemical Engineering, 40(1), 113-125. https://hdl.handle.net/10520/ejc-chemeng-v40-n1-a10 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sajce.2022.02.002
Anbarasu, S., Ilangovan, S., Usharani, K., Prabhabathi, A., Suganya, M., Balamurugan, S., Kayathiri, C., Karthika, M., Nagarethinam, V. S., & Balu, A. R. (2020). Visible light mediated photocatalytic activity of Ni-doped Al2O3 nanoparticles. Surfaces and Interfaces, 18, 100416. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfin.2019.100416 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfin.2019.100416
Arslan, I., Balcioǧlu, I. A., & Bahnemann, D. W. (2000). Advanced chemical oxidation of reactive dyes in simulated dyehouse effluents by ferrioxalate-Fenton/UV-A and TiO2/UV-A processes. Dyes and Pigments, 47(3), 207-218. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0143-7208(00)00082-6 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0143-7208(00)00082-6
Athar, T. (2013). Synthesis and characterization of Strontium oxide nanoparticles via wet process. Materials Focus, 2(6), 450-453. https://doi.org/10.1166/mat.2013.1121 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1166/mat.2013.1121
Chakraborty, R., Vilya, K., Pradhan, M., & Nayak, A. K. (2022). Recent advancement of biomass-derived porous carbon based materials for energy and environmental remediation applications. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 10(13), 6965-7005. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1TA10269A DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/D1TA10269A
Dawoud, T. M., Pavitra, V., Ahmad, P., Syed, A., & Nagaraju, G. (2020). Photocatalytic degradation of an organic dye using Ag doped ZrO2 nanoparticles: Milk powder facilitated eco-friendly synthesis. Journal of King Saud University-Science, 32(3), 1872-1878. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksus.2020.01.040 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksus.2020.01.040
Epold, I., Dulova, N., Veressinina, Y., & Trapido, M. (2012). Application of ozonation, UV photolysis, Fenton treatment and other related processes for degradation of ibuprofen and sulfamethoxazole in different aqueous matrices. Journal of Advanced Oxidation Technologies, 15(2), 354-364. https://doi.org/10.1515/jaots-2012-0215 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1515/jaots-2012-0215
Jadhav, A. H., Patil, S. H., Sathaye, S. D., & Patil, K. R. (2014). A facile room temperature synthesis of ZnO nanoflower thin films grown at a solid–liquid interface. Journal of Materials Science, 49, 5945-5954. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-014-8313-1 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-014-8313-1
Javaid, R., Qazi, U. Y., Ikhlaq, A., & Zahid, M. (2021). Subcritical and supercritical water oxidation for dye decomposition. Journal of Environmental Management, 290, 112605. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.112605 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.112605
Jenifer, A., Sastri, M. S., & Sriram, S. (2021). Photocatalytic dye degradation of V2O5 Nanoparticles—An experimental and DFT analysis. Optik, 243, 167148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2021.167148 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2021.167148
Martha, S., Reddy, K. H., Biswal, N., & Parida, K. (2012). Facile synthesis of InGaZn mixed oxide nanorods for enhanced hydrogen production under visible light. Dalton Transactions, 41(46), 14107-14116. https://doi.org/10.1039/C2DT31949G DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/c2dt31949g
Mishra, P. K., Biswal, S., & Sahu, D. (2022). Synthesis and photocatalytic activity of Ni doped SnO2 nanoparticles for removal of toxic industrial dyes. Materials Today: Proceedings, 68(part 1), 80-84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2022.06.104 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2022.06.104
Mukherji, A., Seger, B., Lu, G. Q. M., & Wang, L. (2011). Nitrogen doped Sr2Ta2O7 coupled with graphene sheets as photocatalysts for increased photocatalytic hydrogen production. ACS Nano, 5(5), 3483-3492. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn102469e DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/nn102469e
Oyarce, E., Roa, K., Boulett., A., Sotelo, S., Cantero-López, P., Sánchez, J., Rivas, B. L. (2021). Removal of dyes by polymer-enhanced ultrafiltration: an overview. Polymers, 13(19), 3450. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13193450 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13193450
Prasad, N., & Karthikeyan, B. (2017). Cu-doping and annealing effect on the optical properties and enhanced photocatalytic activity of ZnO nanoparticles. Vacuum, 146, 501-508. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2017.03.028 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2017.03.028
Robinson, T., McMullan, G., Marchant, R., & Nigam, P. (2001). Remediation of dyes in textile effluent: a critical review on current treatment technologies with a proposed alternative. Bioresource Technology, 77(3), 247-255. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0960-8524(00)00080-8 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0960-8524(00)00080-8
Sahu, O., & Singh, N. (2019). Significance of bioadsorption process on textile industry wastewater. In: The Impact and Prospects of Green Chemistry for Textile Technology, 367-416. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-102491-1.00013-7 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-102491-1.00013-7
Sakthivel, S., Neppolian, B., Shankar, M. V., Arabindoo, B., Palanichamy. M., & Murugesan, V. (2003). Solar photocatalytic degradation of azo dye: comparison of photocatalytic efficiency of ZnO and TiO2. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 77(1), 65-82. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0927-0248(02)00255-6 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0927-0248(02)00255-6
Saleh, S. M. (2019). ZnO nanospheres based simple hydrothermal route for photocatalytic degradation of azo dye. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 211, 141-147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2018.11.065 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2018.11.065
Sasikala, R., Karthikeyan, K., Easwaramoorthy, D., Bilal, I. M., & Rani, S. K. (2016). Photocatalytic degradation of trypan blue and methyl orange azo dyes by cerium loaded CuO nanoparticles. Environmental Nanotechnology, Monitoring & Management, 6, 45-53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enmm.2016.07.001 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enmm.2016.07.001
Shah, M. S. A. S., Zhang, K., Park, A. R., Kim, K. S., Park, N-G., Park, J. H., & Yoo, P. J. (2013). Single-step solvothermal synthesis of mesoporous Ag–TiO 2–reduced graphene oxide ternary composites with enhanced photocatalytic activity. Nanoscale, 5(11), 5093-5101. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3NR00579H DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/c3nr00579h
Subaihi, A., & Naglah, A. M. (2022). Facile synthesis and characterization of Fe2O3 nanoparticles using L-lysine and L-serine for efficient photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue dye. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 15(2), 103613. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2021.103613 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2021.103613
Sun, T., Qiu, J., & Liang, C. (2008). Controllable fabrication and photocatalytic activity of ZnO nanobelt arrays. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 112(3), 715-721. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp710071f DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/jp710071f
Tansakul, C., Laborie, S., & Cabassud, C. (2011). Adsorption combined with ultrafiltration to remove organic matter from seawater. Water Research, 45(19), 6362-6370. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2011.09.024 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2011.09.024
Verma, M., Singh, K. P., & Kumar, A. (2020). Reactive magnetron sputtering based synthesis of WO3 nanoparticles and their use for the photocatalytic degradation of dyes. Solid State Sciences, 99, 105847. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solidstatesciences.2019.02.008 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solidstatesciences.2019.02.008
Wang, Z., Huang, B., Dai, Y., Qin, X., Zhang, X., Wang, P., Liu, H., Yu, J. (2009). Highly photocatalytic ZnO/In2O3 heteronanostructures synthesized by a coprecipitation method. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 113(11), 4612-4617. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp8107683 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/jp8107683
Wiercigroch, E., Szafraniec, E., Czamara, K., Pacia, M. Z., Majzner, K., Kochan, K., Kaczor, A., Baranska, M., & Malek, K. (2017). Raman and infrared spectroscopy of carbohydrates: a review. Spectrochimica acta part a: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 185, 317-335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2017.05.045 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2017.05.045
Zada, A., Khan, M., Hussain, Z., Shah, M. I. A., Ateeq, M., Ullah, M., Ali, N., Shaheen, S., Yasmeen, H., Shah, S. N. A., & Dang, A. (2022). Extended visible light driven photocatalytic hydrogen generation by electron induction from g-C3N4 nanosheets to ZnO through the proper heterojunction. Zeitschrift für Physikalische Chemie, 236(1), 53-66. https://doi.org/10.1515/zpch-2020-1778 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1515/zpch-2020-1778
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Shahid Zaman, Muhammad Kashif, Muffarih Shah, Abdul Hameed, Noor Majeed, Muhammad Ismail, Ilyas Khan, Saif Ullah, Naqash Khan

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
1) Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
2) Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.
3) Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work.


