Responses of sunflower biomass subjected to different water replacements and NPK sources
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14295/cerrado.v2i3.763Keywords:
Helianthus genus, Minerals, Phosphorus, Potassium, Agronomic parametersAbstract
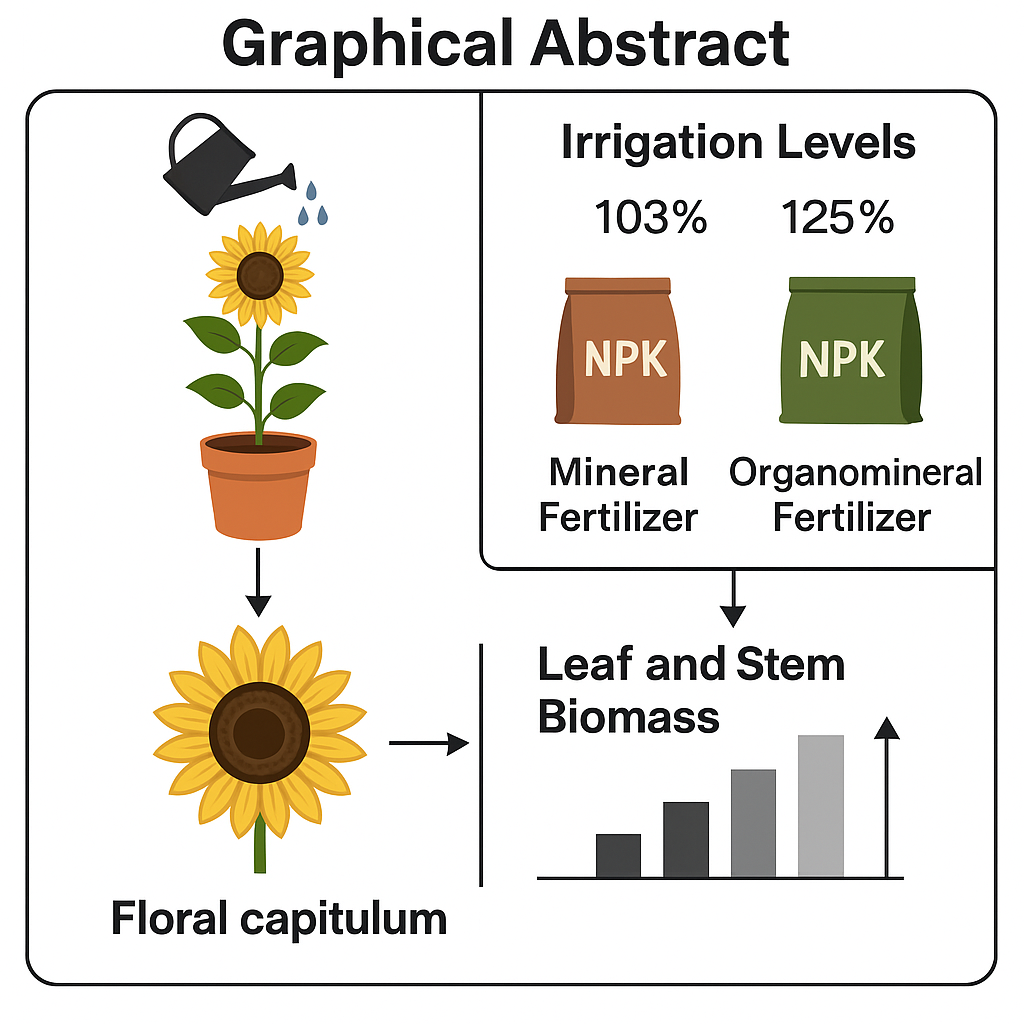
Sunflower is an important agricultural crop with high water demand for optimal development. This study aimed to evaluate the physiological responses of sunflower plants subjected to different irrigation levels and NPK fertilizer sources under protected conditions. The experiment was conducted in pots placed in a greenhouse, with controlled water deficit via lysimeters and application of various doses of NPK fertilizers, in both mineral and organomineral forms. The variables analyzed were fresh mass, dry mass, and water content of the floral capitulum. Results showed that irrigation levels between 103% and 125% led to greater accumulation of dry matter in the leaves and stems. In contrast, increasing NPK doses reduced leaf and stem dry mass, possibly due to toxic effects at doses exceeding crop recommendations. Organomineral fertilization demonstrated a positive effect on the development of leaf and stem biomass. Further studies are recommended to explore the use of alternative natural fertilization strategies in sunflower cultivation.
References
Ahmad, H. M., Wang, X., Mahmood-Ur-Rahman, Fiaz, S., Azeem, F., & Shaheen, T. (2023). Morphological and physiological response of Helianthus annuus L. to drought stress and correlation of wax contents for drought tolerance traits. Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering, 47, 6747-6761. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-06098-1
Alloway, B. J. (2008). Micronutrients and crop production: An introduction. In: Micronutrient Deficiencies in Global Crop Production, Chapter, 1-39 p.
Azevedo, B. M., Vasconcelos, D. V., Bomfim, G. V., Viana, T. V. A., Neto, J. R. N., & Oliveira, K. M. A. S. (2016). Production and yield response factor of sunflower under different irrigation depths. Revista Brasileira de Engenharia Agrícola e Ambiental, 20(5), 427-433. https://doi.org/10.1590/1807-1929/agriambi.v20n5p427-433
Bashir, S., Qayyum, M. A., Husain, A., Bakhsh, A., Ahmed, N., Hussain, M. B., Elshikh, M. S., Alwahbi, M. S., Almunqedhi, B. M. A., Hussain, R., Wang, Y-F., Zhou, Y., & Diao, Z-H. (2021). Efficiency of different types of biochars to mitigate Cd stress and growth of sunflower (Helianthus; L.) in wastewater irrigated agricultural soil. Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences, 28(4), 2453-2459. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.01.045
Coelho, A. M. (2006). Nutrição e adubação do milho. Circular Técnico 78 Ministério da Agricultura, Pecuária e Abastecimento – EMBRAPA, Sete Lagoas, MG, Brasil.
Epstein, E., & Bloom, A. J. (2005). Mineral Nutrition of Plants: Principles and Perspectives (2nd ed.). Sinauer Associates.
Farooq, M., Wahid, A., Kobayashi, N., Fujita, D., & Basra, S. M. A. (2014). Plant drought stress: effects, mechanisms and management. In: Sustainable Agriculture, Springer, 153-188 p.
Ferreira, D. F. (2019). Sisvar: A computer analysis system to fixed effects split plot type designs. Brazilian Journal of Biometrics, 37(4), 529-535. https://doi.org/10.28951/rbb.v37i4.450
Furtado, G. F., Chaves, L. H. G., Souza, L. P., Sousa Júnior, J. R., Lima, G. S., & Sousa, J. R. M. (2017). Índices fisiológicos do girassol em função da adubação com biocarvão e NPK. Revista Brasileira de Agricultura Irrigada, 11(7), 1924-1933.
Furtado, G. F., Silva, M. S. L., & Oliveira, M. B. (2017). Sunflower yield and components in response to NPK doses. Revista de Ciências Agrárias, 40(2), 301-309.
Gomes, E. P., Fedri, G., Ávila, M. R., Biscaro, G. A., Rezende, R. K. S., & Jordan, R. A. (2012). Produtividade de grãos, óleo e massa seca de girassol sob diferentes lâminas de irrigação suplementar. Revista Brasileira de Engenharia Agrícola e Ambiental, 16(3), 237-246.
Hussain, M., Malik, M. A., Farooq, M., Khan, M. B., Akram, M., & Saleem, M. F. (2009). Exogenous glycinebetaine and salicylic acid application improves water relations, allometry and quality of hybrid sunflower under water deficit conditions. Journal of Agronomy and Crop Science, 195(2), 98-109. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-037X.2008.00354.x
Köppen, W., & Geiger, R. (1928). Klimate der Erde. Gotha: Verlag Justus Perthes. Wall-map 150 cm x 200 cm.
Leite, L. F. C., Mendonça, E. S., Neves, J. C. L., Machado, P. L. O. A., & Galvão, J. C. C. (2003). Estoques totais de carbono orgânicos e seus compartimentos em argissolo sob floresta e sob milho cultivado com adubação mineral e orgânica. Revista Brasileira Ciência do Solo, 27, 821-832.
Malaquias, C. A. A., & Santos, A. J. M. (2017). Adubação organomineral e NPK na cultura do milho (Zea mays L.). PUBVET, 11(5), 501-512.
Malavolta, E., Vitti, G. C., & Oliveira, S. A. (1997). Avaliação do estado nutricional das plantas: princípios e aplicações. Potafos.
Marschner, P. (2012). Marschner’s Mineral Nutrition of Higher Plants (3rd ed.). Academic Press.
Rabelo, K. C. C. (2015). Fertilizantes organomineral e mineral: aspectos fitotécnicos na cultura do tomate industrial. Dissertação (Mestrado em Agronomia: Solo e Água). Escola de Agronomia, Universidade Federal de Goiás, Goiânia, 69 f.
Santos, H. G., Jacomine, P. K. T., Anjos, L. H. C., Oliveira, V. A., Lumbreras, J. F., Coelho, M. R., Almeida, J. A., Araujo Filho, J. C., Oliveira, J. B., & Cunha, T. J. F. (2018). Sistema Brasileiro de Classificação de Solos. Brasília: Embrapa, 5ª Ed.
Shafiq, B. A., Nawaz, F., Majeed, S., Aurazgzaib, M., Mamun, A. A., Ahsan, M., Ahmad, K. S., Shehzad, M. A., Ali, M., Hashim, S., & Haq, T. U. (2021). Sulfate-based fertilizers regulate nutrient uptake, photosynthetic gas exchange, and enzymatic antioxidants to increase sunflower growth and yield under drought stress. Journal of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 21, 2229-2241. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-021-00516-x
Soares, L. A. A., Lima, G. S., Chaves, L. H. G., Xavier. D. A., Fernandes, P. D., & Gheyi, H. R. (2015). Fitomassa e produção do girassol cultivado sob diferentes níveis de reposição hídrica e adubação potássica. Revista Brasileira de Engenharia Agrícola e Ambiental, Campina Grande, 19(4),336-342.
Sousa, D. M. G., & Lobato, E. (2004). Cerrado: correção do solo e adubação. 2ª Ed., Brasília: Embrapa Informação Tecnológica/Embrapa-CPA, 2004. 416 p.
Timossi, P. C., Junior, H. I., Lima S. F., Castro R., & Almeida, D. P. (2016). Adubação antecipada com fertilizantes orgânico e mineral associado à crotalarias na cultura do milho. Revista Brasileira de Milho e Sorgo, 15(3).
Yankov, P., & Drumeva, M. (2021). Effect of different types of soil tillage for sunflower on some soil physical characteristics. Part I: soil moisture. Helia, 44(74). https://doi.org/10.1515/helia-2020-0012
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Rafael Borges de Assis, Fernando Rodrigues Cabral Filho, Matheus Vinícius Abadia Ventura, Gustavo Quereza de Freitas, Marconi Batista Teixeira, Nelmício Furtado da Silva, Fernando Nobre Cunha, Christiano Lima Lobo de Andrade

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
1) Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
2) Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.
3) Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work.






